Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
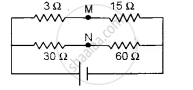
How much resistance should be connected to 15 Ω resistor shown in the circuit in figure below so that the points M and N are at the same potential:
Solution
Let X be the resistance in place of 15 Ω for the points M and N to be at the same potential, then by the condition of balanced wheatstone bridge
`"P"/"Q" = "R"/"S"`
`3/30 = "X"/60`
∴ X = `( 3 xx 60 )/30` = 6 Ω
To make the effective resistance of 6 Ω, let R be a resistance connected in parallel with 15Ω resistance, then
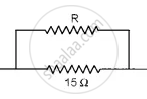
`1/6 = 1/"R" + 1/15`
`1/"R" = 1/6 - 1/15 = ( 5 - 2 )/30 = 3/30`
R = 10 Ω
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Three resistors 2 Ω, 4 Ω and 5 Ω are combined in parallel. What is the total resistance of the combination?
Three identical cells each of emf 2V and internal resistance 10 Ω are connected in series to form a battery. The battery is then connected to a parallel combination of two identical resistors, each of resistance 6 Ω. Find the current delivered by the battery.
Suppose you have three resistors of 20 Ω, 50 Ω and 100 Ω. What minimum and maximum resistance can you obtain from these resistors?
A wire of resistance 15.0 Ω is bent to form a regular hexagon ABCDEFA. Find the equivalent resistance of the loop between the points (a) A and B (b) A and C and (c) Aand D.
Two resistors R1= 60 Ω and R2 = 90Ω are connected in parallel. If electric power consumed by the resistor R1 is15 W, calculate the power consumed by the resistor R2.
If the combination is connected to a battery of emf 20 V and negligible internal resistance, determine the current through each resistor, and the total current drawn from the battery.
Three resistors having values R battery. Suppose R1 carries a current of 2.0 A, R ohms, and R3 dissipates 6.0 watts of power. Then the voltage across R is ______.
If two resistors of resistances R1 = (4 ± 0.5) Ω and R2 = (16 ± 0.5) Ω are connected in series. The eqivalent resistance with the limits of percentage error is ______.
The equivalent resistance of resistors connected in series is always ______
A wire of uniform cross-section and resistance 4 ohms is bent in the shape of square ABCD. Point A is connected to point P on DC by a wire AP of resistance 1 ohm. When a potential difference is applied between A and C, the points B and P are seen to be at the same potential. What is the resistance of the part DP?