Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The breakdown in a reverse biased p–n junction diode is more likely to occur due to ______.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is small.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is large.
- strong electric field in a depletion region if the doping concentration is small.
- strong electric field in the depletion region if the doping concentration is large.
विकल्प
a and d
b and d
c and d
b and c
उत्तर
a and d
Explanation:
Reverse biasing: Positive terminal of the battery is connected to the N-crystal and negative terminal of the battery is connected to P-crystal.
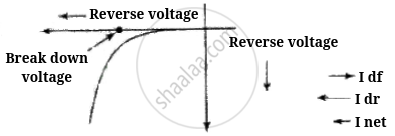
(i) In reverse biasing width of the depletion layer increases
(ii) In reverse biasing resistance offered `R_("Reverse")` = 105 Ω
(iii) Reverse bias supports the potential barrier and no current flows across the junction due to the diffusion of the majority carriers.
(A very small reverse current may exist in the circuit due to the drifting of minority carriers across the junction)
(iv) Break down voltage: Reverse voltage at which break down of semiconductor occurs. For Ge, it is 25 V and for Si, it is 35 V.
So, we conclude that in reverse biasing, ionization takes place because the minority charge carriers will be accelerated due to reverse biasing and striking with atoms which in turn cause secondary electrons and thus more charge carriers.
When doping concentration is large, there will be a large number of ions in the depletion region, which will give rise to a strong electric field.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
With reference to semiconductor devices, define a p-type semiconductor and a Zener diode.
A plate current of 10 mA is obtained when 60 volts are applied across a diode tube. Assuming the Langmuir-Child relation \[i_p \infty V_p^{3/2}\] to hold, find the dynamic resistance rp in this operating condition.
The power delivered in the plate circular of a diode is 1.0 W when the plate voltage is 36 V. Find the power delivered if the plate voltage is increased to 49 V. Assume Langmuir-Child equation to hold.
Diffusion in a p-n junction is due to ______.
Of the diodes shown in the following diagrams, which one is reverse biased?
Consider an npn transistor with its base-emitter junction forward biased and collector base junction reverse biased. Which of the following statements are true?
- Electrons crossover from emitter to collector.
- Holes move from base to collector.
- Electrons move from emitter to base.
- Electrons from emitter move out of base without going to the collector.
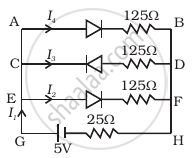
If each diode in figure has a forward bias resistance of 25 Ω and infinite resistance in reverse bias, what will be the values of the current I1, I2, I3 and I4?
A semiconductor device is connected in series with a battery, an ammeter and a resistor. A current flows in the circuit. If. the polarity of the battery is reversed, the current in the circuit almost becomes zero. The device is a/an ______.
Describe briefly the following term:
minority carrier injection in forward biasing.
With reference to a semiconductor diode, define the potential barrier.
