Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
With reference to semiconductor devices, define a p-type semiconductor and a Zener diode.
उत्तर
When a trivalent impurity like aluminium, indium, boron, gallium, etc., is doped with pure germanium
(or silicon) , then the conductivity of the crystal increases due to its deficiency of electrons i.e., holes and such a crystal is said to be p-type semiconductor while the impurity atoms are called acceptors.
A Zener diode is a reverse biased heavily doped p - n junction diode, which is operated in the breakdown region, where the current is limited by both external resistance and power dissipation of the diode.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why is a zener diode considered as a special purpose semiconductor diode?
The plate current in a diode is 20 mA when the plate voltage is 50 V or 60 V. What will be the current if the plate voltage is 70 V?
The dynamic plate resistance of a triode value is 10 kΩ. Find the change in the plate current if the plate voltage is changed from 200 V to 220 V.
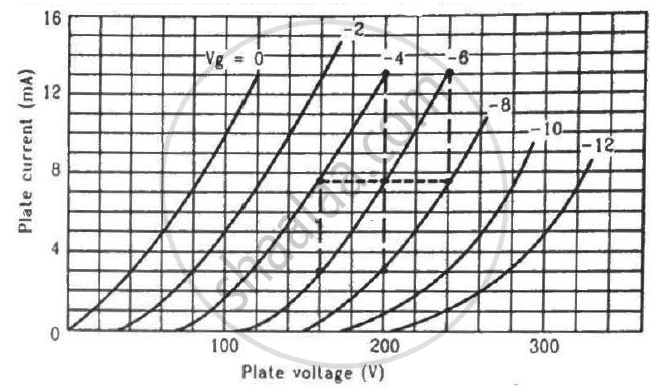
Find the values of rp, µ and gm of a triode operating at plate voltage 200 V and grid voltage −6. The plate characteristics are shown in the figure.
With reference to a semiconductor diode, what is meant by:
(i) Forward bias
(ii) Reverse bias
(iii) Depletion region
The drift current in a p-n junction is from the ______.
On increasing the reverse biases voltage to a large value in a P – N junction diode-current
Avalanche breakdown is due to ______.
A semiconductor device is connected in series with a battery, an ammeter and a resistor. A current flows in the circuit. If. the polarity of the battery is reversed, the current in the circuit almost becomes zero. The device is a/an ______.
Describe briefly the following term:
minority carrier injection in forward biasing.
