Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The power delivered in the plate circular of a diode is 1.0 W when the plate voltage is 36 V. Find the power delivered if the plate voltage is increased to 49 V. Assume Langmuir-Child equation to hold.
Solution
Given:-
When plate voltage, Vp, is 36 V, power delivered in the plate circular of a diode, P, is 1.0 W.
Let the plate current be Ip.
Let the power delivered be P' and plate current be Ip' when plate voltage, Vp, is increased to 49 V
\[ P = I_p V_p \]
\[ \Rightarrow I_p = \frac{P}{V_P} = \frac{1}{36}\]
According to Langmuir-Child equation,
\[I_p \propto ( V_p )^{3/2} , \]
\[ I_p ' \propto ( V_p ' )^{3/2} , \]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{I_p}{I '_p} = \frac{( V_p )^{3/2}}{( V_p ' )^{3/2}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{1/36}{I_p '} = \left( \frac{36}{49} \right)^{3/2} \]
\[ \Rightarrow I_p = 0 . 04411\]
Thus, power delivered when the plate voltage is increased to 49 V,
\[P' = V_p ' \times I_p '\]
\[P' = 49 \times 0 . 04411 W\]
\[P' = 2 . 1613 W = 2 . 2 W\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
With the help of neat labelled circuit diagram explain the working of half wave rectifier using semiconductor diode. Draw the input and output waveforms.
What is the use of Zener diode?
Plot a graph showing variation of current versus voltage for the material GaAs ?
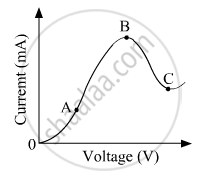
The graph shown in the figure represents a plot of current versus voltage for a given semiconductor. Identify the region, if any, over which the semiconductor has a negative resistance.
Why is a zener diode considered as a special purpose semiconductor diode?
A plate current of 10 mA is obtained when 60 volts are applied across a diode tube. Assuming the Langmuir-Child relation \[i_p \infty V_p^{3/2}\] to hold, find the dynamic resistance rp in this operating condition.
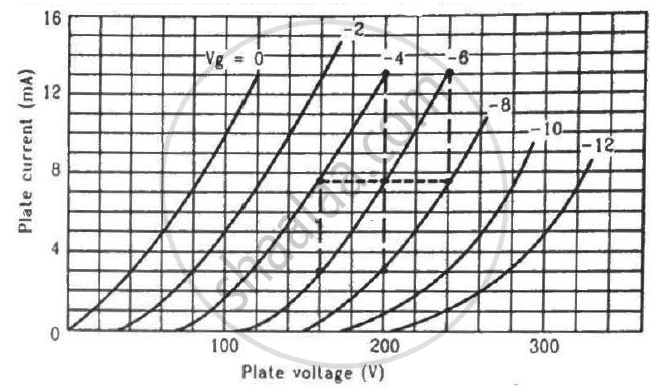
Find the values of rp, µ and gm of a triode operating at plate voltage 200 V and grid voltage −6. The plate characteristics are shown in the figure.
Diffusion in a p-n junction is due to ______.
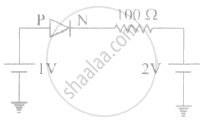
The current through an ideal PN-junction shown in the following circuit diagram will be:
When we apply reverse biased to a junction diode, it
In a semiconductor diode, the barrier potential offers opposition to only
When an electric field is applied across a semiconductor ______.
- electrons move from lower energy level to higher energy level in the conduction band.
- electrons move from higher energy level to lower energy level in the conduction band.
- holes in the valence band move from higher energy level to lower energy level.
- holes in the valence band move from lower energy level to higher energy level.
Figure shows the transfer characteristics of a base biased CE transistor. Which of the following statements are true?

At Vi = 0.4 V, transistor is in active state.
At Vi = 1 V, it can be used as an amplifier.
At Vi = 0.5 V, it can be used as a switch turned off.
At Vi = 2.5 V, it can be used as a switch turned on.
In the depletion region of a diode ______.
- there are no mobile charges.
- equal number of holes and electrons exist, making the region neutral.
- recombination of holes and electrons has taken place.
- immobile charged ions exist.
The breakdown in a reverse biased p–n junction diode is more likely to occur due to ______.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is small.
- large velocity of the minority charge carriers if the doping concentration is large.
- strong electric field in a depletion region if the doping concentration is small.
- strong electric field in the depletion region if the doping concentration is large.
Answer the following giving reasons:
A p-n junction diode is damaged by a strong current.
Describe briefly the following term:
breakdown voltage in reverse biasing
With reference to a semiconductor diode, define the depletion region.
