Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the figure, ΔPQR is right angled at Q, seg QS ⊥ seg PR. Find x, y.

Sum
Solution
Given: ΔPQR = 90°, seg QS ⊥ seg PR.
According to the geometric mean theorem,
QS2 = PS × RS
or QS = `sqrt(PS xx RS)`
= `sqrt(10 xx 8)`
= `sqrt(2 xx 5 xx 2 xx 2 xx 2)`
= `4sqrt(5)`
In ΔQRS, by Pythagoras theorem,
QS2 = QS2 + SR2
= `(4sqrt(5))^2 + (8)^2`
= 80 + 64
= 144
⇒ QR = `sqrt(144)` = 12
Hence, x = `4sqrt(5)`, y = 12.
shaalaa.com
Theorem of Geometric Mean
Is there an error in this question or solution?
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
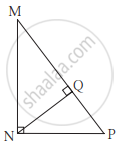
In the given figure, ∠MNP = 90°, seg NQ ⊥ seg MP, MQ = 9, QP = 4, find NQ.
In the given figure, ∠QPR = 90°, seg PM ⊥ seg QR and Q–M–R, PM = 10, QM = 8, find QR.

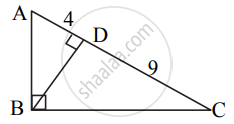
In right-angled ΔABC, BD ⊥ AC. If AD= 4, DC= 9, then find BD.
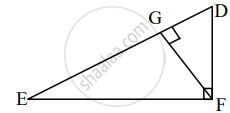
As shown figure, ∠DFE = 90°, FG ⊥ ED, if GD = 8, FG = 12, then EG = ?