Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the given figure, chord AB ≅ chord CD, Prove that, arc AC ≅ arc BD.
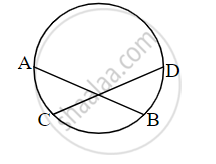
Solution
Chord AB ≅ Chord CD ...(Given)
∴ Arc ACB ≅ Arc CBD ...(Arcs corresponding to congruent chords.)
∴ m(arc ACB) = m(arc CBD) ...(1)
But m(arc ACB) = m(arc AC) + m(arc CB) ...(2)
and m(arc CBD) = m(arc CB) + m(arc BD) ...(3)
From (1), (2), and (3), we get,
m(arc AC) + m(arc CB) = m(arc CB) + m(arc BD)
∴ m(arc AC) = m(arc BD)
∴ arc AC ≅ arc BD
Hence, proved.
RELATED QUESTIONS
In the given figure, ∆QRS is an equilateral triangle. Prove that,
- arc RS ≅ arc QS ≅ arc QR
- m(arc QRS) = 240°.

In the given figure, in a circle with centre O, length of chord AB is equal to the radius of the circle. Find measure of each of the following.
(1) ∠ AOB (2)∠ ACB
(3) arc AB (4) arc ACB.
Four alternative answers for the following question is given. Choose the correct alternative
In a cyclic ▢ABCD, twice the measure of ∠A is thrice the measure of ∠C. Find the measure of ∠C?
Four alternative answers for the following question is given. Choose the correct alternative.
Points A, B, C are on a circle, such that m(arc AB) = m(arc BC) = 120°. No point, except point B, is common to the arcs. Which is the type of ∆ABC?
`square`PQRS is a parallelogram. Write the sum of measures of ∠P and ∠ Q.
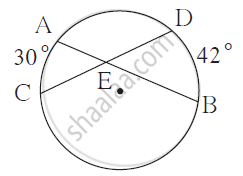
From the information given in the figure, find the measure of ∠ AEC.
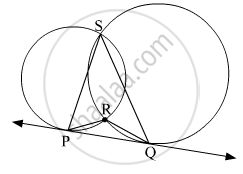
In the given figure, two circles intersect each other at points S and R. Their common tangent PQ touches the circle at points P, Q.
Prove that, ∠ PRQ + ∠ PSQ = 180°
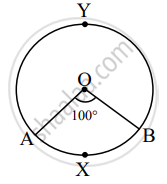
In the figure given above, O is the centre of the circle. Using given information complete the following table:
| Type of arc | Name of the arc | Measure of the arc |
| Minor arc | `square` | `square` |
| Major arc | `square` | `square` |
What is the measure of a semi circular arc?
In figure, in a circle with center O, the length of chord AB is equal to the radius of the circle. Find the measure of the following.
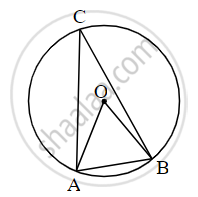
(i) ∠AOB
(ii) ∠ACB
(iii) arc AB.
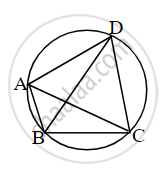
In the figure, quadrilateral ABCD is cyclic. If m(arc BC) = 90° and ∠DBC = 55°, then find the measure of ∠BCD.
Chord AB and chord CD of a circle with centre 0 are congruent. If m(arc AB) = 120°, then find the m(arc CD).
