Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
…………. is a mode of asexual reproduction.
(a) Cloning
(b) Budding
(c) Pollination
(d) Germination
Solution
(b) Budding.
Cloning is a process by which an entire organism is reproduced in a genetically identical manner from a single cell taken from the parent organism. Pollination and germination are associated with sexual reproduction in plants.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw labelled diagrams to illustrate budding in Hydra.
How does multiple fission occur in an organism? Explain briefly.
Explain the process of regeneration in Planaria.
How will an organism be benefited if it reproduces through spores?
A tadpole develops into an adult frog by the process of ______.
Draw in sequence (showing the four stages), the process of binary fission in Amoeba.
Describe reproduction by spores in Rhizopus
Name the process by which an Amoeba reproduces. Draw the various stages of its reproduction in a proper sequence.
Name one organism which reproduces by binary fission and another which reproduces by multiple fission.
State whether the above named organisms are animals or plants.
Why does bread mould grow profusely on a moist slice of bread but not on a dry slice of bread?
Explain how new Bryophyllum plants can be produced from the leaves of the old plant. Illustrate your answer with the help of a labelled diagram.
What is the difference between the two asexual methods of reproduction : fission and fragmentation?
Describe the grafting method for the artificial propagation of plants with the help of labelled diagrams.
The two types of organisms which produce colonies by the process of budding are :
(a)Hydra and Corals
(b) Yeast and Sponges
(c) Corals and Sponges
(d) Hydra and Yeast
An organism having a whip-like structure at one end which reproduces by the process of binary fission is :
(a) Hydra
(b) Paramecium
(c) Leishmania
(d) Plasmodium
APlanaria worm is cut horizontally in the middle into two halves P and Q such that the part P contains the whole head of the worm. Another Planaria worm is cut vertically into two halves R and s in such a way that both the cut pieces R and S contain half head each. Which of the cut pieces of the twoPlanaria worms could regenerate to form the complete respective worms?
(a) only P
(b) only R and S
(c) P, R and S
(d) P, Q, R and S
Two very small organisms X and Y both reproduce by the method of budding. Organism X is industrially very important because it is used in making alcohol from sugar. It is also used in making bread. Organism Y Lives in freshwater. If organism Y gets cut into a number of parts accidently, each cut part can grow to form complete organism.
(a) What are organisms X and Y?
(b) What is the name of the process in which X converts sugar into alcohol?
(c) To which class of organisms does X belong?
(d) Name an important body feature of organism Y.
(e) Which organism is multicellular and which one is unicellular?
A filamentous alga X is found in ponds, lakes and slow-moving streams. The filament of this alga simply breaks into two (or more) pieces on maturing and each piece then grows to become a complete new alga.
(a) Name an alga which X is likely to be.
(b) What is the colour of X?
(c) What is the method of forming new algae by the breaking of parent alga known as?
(d) An Amoeba also breaks up to form two daughter Amoebae. What is the difference in the splitting of Amoeba and splitting of this alga as a method of reproduction?
(e) Name one marine animal which reproduces in the same way as alga X.
Fill in the blank:
Budding produces cells of __________ size.
State whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F):
Cutting and grafting are natural means of reproduction.
Explain the process of binary fission in bacteria.
A student after viewing a prepared slide illustrates the budding in yeast in the following order which is not correct:

(A) b, c, d, e, a
(B) b, e, d, c, a
(C) b, d, e, c, a
(D) b, d, c, e, a
In which of the following figures is budding not shown?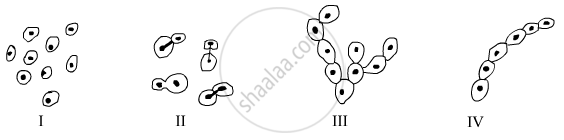
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
A student was given two permanent slides, one of binary fission in Amoeba and other of budding in yeast. He was asked to identify any one difference in the nucleus of the two. One such difference, he identified correctly was
(1) Presence of one nucleus in Amoeba, two in yeast cell and one in bud.
(2) Presence of two nuclei in centrally constricted Amoeba, one in yeast cell and one in its bud.
(3) Presence of two distant nuclei in Amoeba, one in yeast cell and two in bud.
(4) Presence of a single nucleus each in Amoeba, yeast cell and its attached bud.
Complete the following chart:
| Asexual reproduction | Sexual reproduction | ||
| 1. | Reproduction that occurs with the help of somatic cells is called as asexual reproduction. | 1. | ____________ |
| 2. | ____________ | 2. | Male and female parent are necessary for sexual reproduction. |
| 3. | This reproduction occurs with the help of mitosis only. | 3. | ____________ |
| 4 | ____________ | 4. | New individual formed by this method is genetically different from parents. |
| 5 | Asexual reproduction occurs in different individuals by various methods like binary fission, multiple fission, budding, fragmentation, regeneration, vegetative propagation, spore production, etc. | 5. | ____________ |
Explain asexual reproduction in plants.
In hydra the type of reproduction is ___________.
Why is chemical communication better than electrical impulses as a means of communication between cells in a multi-cellular organism?
Write various advantages of vegetative propagation.
Name four plants which can be propagated by stem-cutting.
Write four lines on the following: Grafting
Name the parts of the plants used to grow following flower: Gladiolus
What is micropropagation?
Write a note on different types of endosperms in angiosperms.
Which of the following is not a type of asexual reproduction in multicellular organisms?
Draw a neat and labelled diagram.
Spore formation
Many unicellular organisms reproduce by the process of ______
Vegetative propagation refers to formation of new plants from
Rajesh observed a patch of greenish black powdery mass on a stale piece of bread.
Name its vegetative and reproductive parts.
