Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Enlist and write in brief about the different biological tools required in rDNA technology.
Solution
The different biological tools required in rDNA technology:
i. Instruments: PCR, Agarose Gel Electrophoresis, SDS-PAGE
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is the process of in vitro amplification of the gene of interest using a PCR machine.
- PCR can generate a billion copies of the desired segment of DNA or RNA, with high accuracy and specificity, in a few hours.
- The process of PCR is completely automated and involves automatic thermal cycles for denaturation and renaturation of double-stranded DNA.
- The device required for PCR is called a thermal cycler.
Requirements for polymerase chain reaction:
- DNA containing the desired segment to be amplified
- several molecules of four deoxyribonuclueoside triphosphates (dNTPs)
- excess of two primer molecules
- heat-stable DNA polymerase and
- appropriate quantities of Mg++ ions.
DNA replication through a polymerase chain reaction.
ii. Biological tools: Enzymes, Cloning Vectors, Competent host
Different enzymes used in rDNA technology are as follows: Lysozymes, Nucleases such as exonucleases, endonucleases, restriction endonucleases, DNA ligases, DNA polymerases, alkaline phosphatases, reverse transcriptase, etc.
- Enzymes that cut the phosphodiester bonds of polynucleotide chains are called nuclease.
- These are of two types- exonuclease and endonuclease.
- Exonucleases cut nucleotides from the ends of DNA strands whereas endonuclease cut DNA from within.
- The phosphodiester backbone at highly specific sites on both strands of the duplex is cut by these enzymes called restriction endonucleases or simply restriction enzymes.
- The restriction enzymes are thus the molecular scissors that are used to recognize and cut DNA at specific sequences.
- The sites recognized by them, are called recognition sequences or recognition sites.
- Different restriction enzymes found in different organisms recognize different nucleotide sequences and therefore cut DNA at different sites.
The following characteristic properties a cloning vector must possess in order to be used in rDNA technology:
- A good vector should have the ability of independent replication so that as the vector replicates (through ori gene) and a large number of copies of the DNA insert will be formed.
- The vector should be able to easily introduce into host cells.
- A vector should have marker genes for antibiotic resistance.
- A vector must contain a unique cleavage site in one of the marker genes for the restriction enzyme.
- It should have at least suitable control elements like a promoter, operator, ribosomal binding sites, etc.
- The plasmids obtained naturally do not possess all the characteristics. Hence, they are constructed by inserting a gene for antibiotic resistance. e.g. pBR322, pBR320, pACYC177 are the constructed plasmids. pBR322 is mostly used in rDNA technology in plants.
Competent hosts (cloning organisms) used are usually bacteria like Bacillus haemophilus, Helicobacter pylori, and E. coli. Mostly E. coli is used for the transformation with recombinant DNA.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
One of the major contributions of biotechnology is to develop pest-resistant varieties of cotton plants. Explain how it has been made possible.
Explain the mechanism of action of restriction endonucleases that makes them suitable for genetic engineering.
What is the cell that receives a recombinant gene called?
Explain the properties of a good or ideal cloning vector for rDNA technology.
For which of the following purpose restriction endonuclease enzyme is used in genetic engineering?
From the following identify the methods of electrophoresis.
Which of the following is not required in the preparation of a recombinant DNA molecule?
Observe the given sequence of nitrogenous bases on a DNA fragments and answer the following questions:
5' - CAGAATTCTTA - 3'
3' - GTCTTAAGAAT - 5'
- Name a restriction enzyme which can recognise this DNA sequence.
- Write the sequence after digestion.
- Why are the ends generated after digestion called sticky ends?
What is polymerase chain reaction (PCR)?
The structure below shows pUC18, which is similar to pBR322 in its function. However, they differ in some of their restriction sites and the number of ori. The ori number for pBR322 is approximately 20.
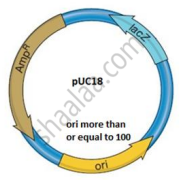
- How are puc18 and pBR322 used in biotechnological studies?
OR
What will be the impact if the ori in the above structure gets damaged? - The lac z gene has many recognition sites. Study the segment of DNA given below and answer the questions.
5’... ATC GTA AAG CTT CAT…3’
3’... TAG CAT TTC GAA GTA…5’
i) Applying your knowledge of palindrome sequences identify and mark the possible region where the restriction enzyme X will act.
ii) Restriction enzyme Y was used to extract a gene of interest from a plant. This gene needs to be inserted in the given DNA segment which has been treated with restriction enzyme X. Will there be a successful recombination? Explain with a reason. - Which one of the two (pUC18 and pBR322) would you prefer for biotechnological studies? Justify.
