Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Name the Following
The branch of renal artery which enters into Bowman’s capsule.
Solution
Afferent arteriole
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name the Following
The organ which produces urea.
Write True (T) or False (F) for the following statement. Rewrite the false statement in the correct form.
Urine is devoid of blood cells.
State if the following statement is true or false. Correct the statement if it is false.
Liver produces bile pigments from the hemoglobin of broken RBCs.
In humans, urea is formed in
Look at the figure given below. It is a section of human kidney as seen from the front.
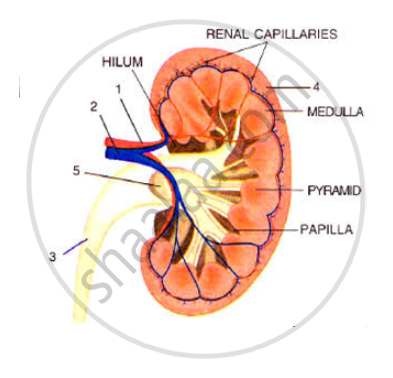
Which area/part (give its name and number given on the diagram) which contains the following:
(i) Malpighian capsule
(ii) The pyramids
(iii) Freshly collected urine
The following diagram represents a mammalian kidney tubule (nephron) and its blood supply.
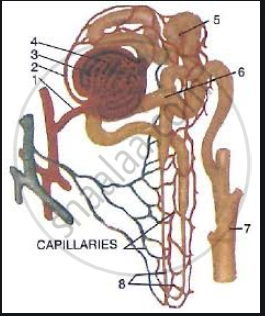
Parts indicated by the guidelines 1to 8 are as follows:
1. Afferent arteriole from renal artery
2. Efferent arteriole
3. Bowman's capsule
4. Glomerulus
5. Proximal convoluted tubule with blood capillaries
6. Distal convoluted tubule with blood capillaries
7. Collecting tubule
8. U-shaped loop of Henle
Study the diagram and answer the question that follow:
Which structure contains the highest concentration of urea?
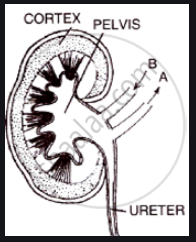
Given below is a highly simplified diagram of the human kidney cut open longitudinally. Answer the question that follow:
Why does the cortex of the kidney show a dotted appearance?
Study the diagram given below and then answer the questions that follow:
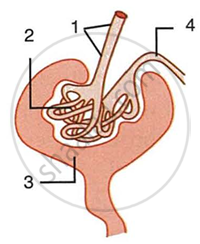 |
- Name the region in the kidney where the above structure is present?
- Name the parts labelled 1, 2, 3 and 4.
- Name the stages involved in the formation of urine.
- What is the technical term given to the process occurring in 2 and 3? Briefly describe the process.
What would happen if green plants disappeared from earth?
Given below is a list of substances - select the ones that need to be eliminated from the body.
Glucose, excess water, amino acids, urea, carbon dioxide, excess common salt, glycogen, uric acid.
