Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Obtain an expression for electric field intensity at a point outside uniformly charged thin plane sheet.
Solution
Expression for electric intensity due to uniformly charged infinite plane sheet:
a. Consider an infinite thin plane sheet of positive charge having a uniform surface charge density σ on both sides of the sheet.
b. By symmetry, it follows that the electric field is perpendicular to the plane sheet of charge and is directed in outward direction.
c. Electric field intensity has same magnitude at a given distance on either sides of the sheet.
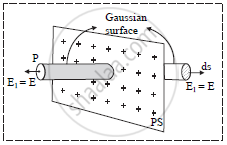
d. To find electric field intensity at a point P due to uniformly charged infinite thin plane sheet, construct an imaginary cylinder around P with its axis perpendicular to plane sheet carrying charge with ends having cross sectional area ds.
e. The plane sheet passes through the middle of cylinder’s length so that the ends of cylinder are equidistant from the plane sheet carrying charge.
f. Electric field intensity, `vecE` is perpendicular to the ends of cylinder, hence the electric flux through each end is Eds.
g. Since `vecE` is perpendicular to plane sheet, it is parallel to the curved surface of Gaussian cylinder. Hence, electric flux does not pass through the curved surface of Gaussian cylinder.
h. Now, Total Normal Electric Induction over Gaussian surface = ε E (2ds)
where, ds is surface area of end faces of the cylinder.
Algebraic sum of charges enclosed by Gaussian cylinder = σds
According to Gauss’ law,
ε E (2ds) = σds
E =σ/2ε
This is the expression for electric field intensity at a point outside uniformly charged thin plane sheet.
j. Above equation shows that the magnitude of electric field intensity is independent of the distance of point from plane sheet.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
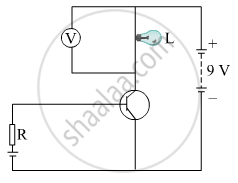
In the given circuit diagram a voltmeter ‘V’ is connected across a lamp ‘L’. Ho would (i) the brightness of the lamp and (ii) voltmeter reading ‘V’ be affected, if the value of resistance ‘R’ is decreased? Justify your answer.
A 10 V battery of negligible internal resistance is connected across a 200 V battery and a resistance of 38Ω as shown in the figure. Find the value of the current in circuit.

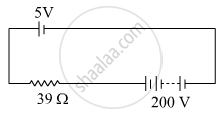
A 5 V battery of negligible internal resistance is connected across a 200 V battery and a resistance of 39Ω as shown in the figure. Find the value of the current in circuit.
If the above capacitor is connected across a 6⋅0 V battery, find (a) the charge supplied by the battery, (b) the induced charge on the dielectric and (c) the net charge appearing on one of the coated surfaces.
A capacitor has some dielectric between its plates, and the capacitor is connected to a dc source. The battery is now disconnected and then the dielectric is removed, then ______.
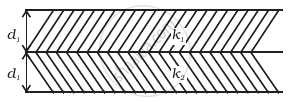
A parallel plate capacitor is made of two dielectric blocks in series. One of the blocks has thickness d1 and dielectric constant k1 and the other has thickness d2 and dielectric constant k2 as shown in figure. This arrangement can be thought as a dielectric slab of thickness d (= d1 + d2) and effective dielectric constant k. The k is ______.
A capacitor is made of two circular plates of radius R each, separated by a distance d << R. The capacitor is connected to a constant voltage. A thin conducting disc of radius r<<R and thickness t << r is placed at a centre of the bottom plate. Find the minimum voltage required to lift the disc if the mass of the disc is m.
