Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Obtain the law of radioactivity.
Solution
At any instant t, the number of decays per unit time, called rate of decay `("dN"/"dt")` is proportional to the number of nuclei (N) at the same instant.
`"dN"/"dt" prop "N"`
By introducing a proportionality constant, the relation can be written as
`"dN"/"dt" = - lambda"N"`
Here proportionality constant λ is called decay constant which is different for different radioactive sample and the negative sign in the equation implies that the N is decreasing with time. By rewriting the equation (1), we get
dN = - λNdt …… (2)
Here dN represents the number of nuclei decaying in the time interval dt. Let us assume that at time t =0 s, the number of nuclei present in the radioactive sample is N0. By integrating the equation (2), we can calculate the number of undecayed nuclei N at any time t. From equation (2), we get
`"dN"/"N"` = - λNdt ....(3)
\[\int\limits_{N_0}^N\] `"dN"/"N"` = - `int_0^"t" lambda "dt"`
`["In N"]_("N"_0)^("N")` = - λt
In `["N"/"N"_0]` = - λt
Law of radioactive decay
Taking exponentials on both sides, we get
N = N0 e-λt ….. (4)
[Note: eInx = ey ⇒ x = ey]
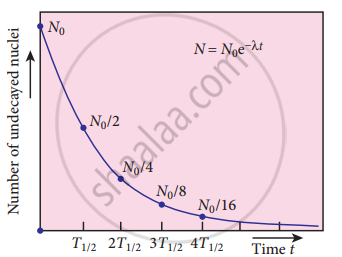
Equation (4) is called the law of radioactive decay. Here N denotes the number of undecayed nuclei present at any time t and N0 denotes the number of nuclei at initial time t = 0. Note that the number of atoms is decreasing exponentially over time. This implies that the time taken for all the radioactive nuclei to decay will be infinite. Equation (4) is plotted.
We can also define another useful quantity called activity (R) or decay rate which is the number of nuclei decayed per second and it is denoted as R = `|"dN"/"dt"|`
Note: that activity R is a positive quantity. From equation (4), we get
R = `|"dN"/"dt"|` = λ N0 e-λt ….. (5)
R = R0 e-λt ….. (6)
Where R = λ N0
The equation (6) is also equivalent to the radioactive law of decay. Here R0 is the activity of the sample at t = 0 and R is the activity of the sample at any time t. From equation (6), activity also shows exponential decay behavior. The activity R also can be expressed in terms of a number of undecayed atoms present at any time t. From equation (6), since N = N0 e-λt we write
R = λ N …… (7)
Equation (4) implies that the activity at any time t is equal to the product of decay constant and the number of undecayed nuclei at the same time t. Since N decreases over time, R also decreases.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write two units of radioactivity. How are they interrelated?
In alpha decay, why the unstable nucleus emits \[\ce{^4_2He}\] nucleus? Why it does not emit four separate nucleons?
What is mean life of nucleus? Give the expression.
What are the constituent particles of neutron and proton?
Discuss the beta decay process with examples.
Half-lives of two radioactive elements A and B are 20 minutes and 40 minutes respectively. Initially, the samples have equal number of nuclei. Calculate the ratio of decayed numbers of A and B nuclei after 80 minutes.
Characol pieces of tree is found from an archeological site. The carbon-14 content of this characol is only 17.5% that of equivalent sample of carbon from a living tree. What is the age of tree?
Mean life (τ) of a radioactive substance is x times of its half-life (t). Here x is:
The radio active decay of uranium into thorium is expressed by the 92U238 `->` 90Th234 + x where x is
The half-life period of a radioactive substance is 5 min. The amount decayed in 20 min will be
