Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
On addition of small amount of \[\ce{KMnO4}\] to concentrated \[\ce{H2SO4}\], a green oily compound is obtained which is highly explosive in nature. Identify the compound from the following.
Options
\[\ce{Mn2O7}\]
\[\ce{MnO2}\]
\[\ce{MnSO4}\]
\[\ce{Mn2O3}\]
Solution
\[\ce{Mn2O7}\]
Explanation:
\[\ce{2KMnO4 + 2H2SO4 (Conic) -> Mn2O7 + 2KHO4 + H2O}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Complete the following equations:
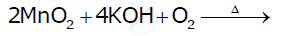
Complete the following equations: Cr2O72- + 14H+ + 6I →
When chromite ore FeCr2O4 is fused with NaOH in presence of air, a yellow-coloured compound (A) is obtained, which on acidification with dilute sulphuric acid gives a compound (B). Compound (B) on reaction with KCl forms an orange coloured crystalline compound (C).
(i) Write the formulae of the compounds (A), (B) and C.
(ii) Write one use of compound (C).
Complete the following equations : 2 MnO2 + 4 KOH + O2 →
Complete the following chemical equations :
Cu + H2SO4(conc.) →
Using IUPAC norms write the formulae of Potassium trioxalatochromate (III)
In the form of dichromate, \[\ce{Cr (VI)}\] is a strong oxidising agent in acidic medium but \[\ce{Mo (VI)}\] in \[\ce{MoO3}\] \[\ce{and W (VI)}\] in \[\ce{WO3}\] are not because:
(i) \[\ce{Cr(VI)}\] is more stable than \[\ce{Mo(VI)}\] and \[\ce{and W(VI)}\].
(ii) \[\ce{Mo(VI)}\] and \[\ce{and W(VI)}\] are more stable than \[\ce{Cr(VI)}\].
(iii) Higher oxidation states of heavier members of group-6 of transition series are more stable.
(iv) Lower oxidation states of heavier members of group-6 of transition series are more stable.
When orange solution containing \[\ce{Cr2O^{2-}7}\] ion is treated with an alkali, a yellow solution is formed and when \[\ce{H^+}\] ions are added to yellow solution, an orange solution is obtained. Explain why does this happen?
Why \[\ce{HCl}\] should not be used for potassium permanganate titrations?
Indicate the steps in the preparation of \[\ce{K2Cr2O7}\] from chromite ore.
