Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Only one of the following applies to a concave lens. This is:
(a) focal length is positive
(b) image distance can be positive or negative
(c) height of image can be positive or negative
(d) image distance is always negative
Solution
image distance is always negative
Because a concave lens always forms a virtual image on the left side of the lens.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If the image formed by a lens for all positions of an object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what is the nature of this lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer.
Explain with the help of a diagram, why the concave lens is also called a diverging lens.
What type of image is always made by a concave lens?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Lenses refract light to form images: a..................... lens can form both real and virtual images, but a diverging lens forms only ...................... images.
An object is placed 10 cm from a lens of focal length 5 cm. Draw the ray diagrams to show the formation of image if the lens is diverging.
When an object is kept at any distance in front of a concave lens, the image formed is always:
(a) virtual, erect and magnified
(b) virtual, inverted and diminished.
(c) virtual, erect and diminished
(d) virtual, erect and same size as object
A beam of light is incident through the holes on one side of a box and emerges out through the holes on its opposite side as shown in the following figure:
The box contains:
(a) a glass prism
(b) a concave lens
(c) a convex lens
(d) a parallel-sided glass slab
Study the diagram below.
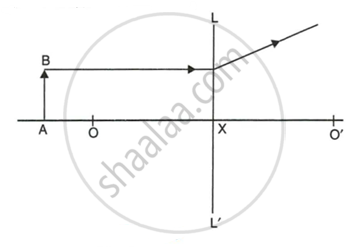
- Name the lens LL’.
- What are the points O and O' called ?
- Complete the diagram to form the image of the object AB.
- State three characteristics of the image.
A student obtained clear image of window grills on the screen. But the teacher told him to get the image of a tree far away, instead of window. To get a clear image, the lens must be ............................
When an object is kept within the focus of a concave mirror, an enlarged image is formed behind the mirror. This image is :
