Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Find the minimum colatitude which can directly receive a signal from a geostationary satellite.
Solution
Consider that B is the position of the geostationary satellite.
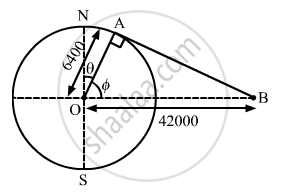
In the given figure,
In triangle OAB, we have:
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two satellites A and B move round the earth in the same orbit. The mass of B is twice the mass of A.
A body stretches a spring by a particular length at the earth's surface at the equator. At what height above the south pole will it stretch the same spring by the same length? Assume the earth to be spherical.
At what rate should the earth rotate so that the apparent g at the equator becomes zero? What will be the length of the day in this situation?
A Mars satellite moving in an orbit of radius 9.4 × 103 km takes 27540 s to complete one revolution. Calculate the mass of Mars.
Answer the following question in detail.
What is a critical velocity?
Describe how an artificial satellite using a two-stage rocket is launched in an orbit around the Earth.
Calculate the kinetic energy, potential energy, total energy and binding energy of an artificial satellite of mass 2000 kg orbiting at a height of 3600 km above the surface of the Earth.
Given: G = 6.67 × 10-11 Nm2/kg2
R = 6400 km, M = 6 × 1024 kg
Solve the following problem.
Calculate the speed of a satellite in an orbit at a height of 1000 km from the Earth’s surface.
(ME = 5.98 × 1024 kg, R = 6.4 × 106 m)
What is the minimum energy required to launch a satellite of mass 'm' from the surface of the earth of mass 'M' and radius 'R' at an altitude 2R?
An aircraft is moving with uniform velocity 150 m/s in the space. If all the forces acting on it are balanced, then it will ______.
If a body weighing 40 kg is taken inside the earth to a depth to radius of the earth, then
Reason of weightlessness in a satellite is ____________.
A geostationary satellite is orbiting the earth at the height of 6R above the surface of earth. R being radius of earth. The time period of another satellite at a height of 2.5 R from the surface of earth is ____________.
A satellite of mass 'm', revolving round the earth of radius 'r' has kinetic energy (E). Its angular momentum is ______.
A satellite of mass 'm' is revolving around the earth of mass 'M' in an orbit of radius 'r' with constant angular velocity 'ω'. The angular momentum of the satellite is ______.
(G =gravitational constant)
In the case of earth, mean radius is 'R', acceleration due to gravity on the surface is 'g', angular speed about its own axis is 'ω'. What will be the radius of the orbit of a geostationary satellite?
A satellite is revolving in a circular orbit at a height 'h' above the surface of the earth of radius 'R'. The speed of the satellite in its orbit is one-fourth the escape velocity from the surface of the earth. The relation between 'h' and 'R' is ______.
A satellite revolves around a planet very close to its surface. By what maximum factor can its kinetic energy be increased suddenly, such that it revolves in orbit in the same way?
