Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The pressure of a gas kept in an isothermal container is 200 kPa. If half the gas is removed from it, the pressure will be
Options
100 kPa
200 kPa
400 kPa
800 kPa
Solution
100 kPa
Let the number of moles in the gas be n.
Applying equation of state, we get
=100 kPa
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
From a certain apparatus, the diffusion rate of hydrogen has an average value of 28.7 cm3 s–1. The diffusion of another gas under the same conditions is measured to have an average rate of 7.2 cm3 s–1. Identify the gas
[Hint: Use Graham’s law of diffusion: R1/R2 = (M2/M1)1/2, where R1, R2 are diffusion rates of gases 1 and 2, and M1 and M2 their respective molecular masses. The law is a simple consequence of kinetic theory.]
While gas from a cooking gas cylinder is used, the pressure does not fall appreciably till the last few minutes. Why?
Explain why cooking is faster in a pressure cooker.
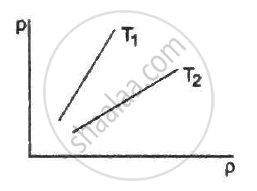
Figure shows graphs of pressure vs density for an ideal gas at two temperatures T1 and T2.
Equal masses of air are sealed in two vessels, one of volume V0 and the other of volume 2V0. If the first vessel is maintained at a temperature 300 K and the other at 600 K, find the ratio of the pressures in the two vessels.
Use R = 8.31 JK-1 mol-1
Figure shows a cylindrical tube with adiabatic walls and fitted with a diathermic separator. The separator can be slid in the tube by an external mechanism. An ideal gas is injected into the two sides at equal pressures and equal temperatures. The separator remains in equilibrium at the middle. It is now slid to a position where it divides the tube in the ratio of 1:3. Find the ratio of the pressures in the two parts of the vessel.
Use R=8.314J K-1 mol-1

Air is pumped into an automobile tyre's tube up to a pressure of 200 kPa in the morning when the air temperature is 20°C. During the day the temperature rises to 40°C and the tube expands by 2%. Calculate the pressure of the air in the tube at this temperature.
Is a slow process always isothermal? Is a quick process always adiabatic?
In an adiabatic process on a gas with γ = 1.4, the pressure is increased by 0.5%. The volume decreases by about
An ideal gas is kept in a long cylindrical vessel fitted with a frictionless piston of cross-sectional area 10 cm2 and weight 1 kg. The length of the gas column in the vessel is 20 cm. The atmospheric pressure is 100 kPa. The vessel is now taken into a spaceship revolving round the earth as a satellite. The air pressure in the spaceship is maintained at 100 kPa. Find the length of the gas column in the cylinder.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
On a winter day, the outside temperature is 0°C and relative humidity 40%. The air from outside comes into a room and is heated to 20°C. What is the relative humidity in the room? The saturation vapour pressure at 0°C is 4.6 mm of mercury and at 20°C it is 18 mm of mercury.
The temperature and humidity of air are 27°C and 50% on a particular day. Calculate the amount of vapour that should be added to 1 cubic metre of air to saturate it. The saturation vapour pressure at 27°C = 3600 Pa.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
The temperature and relative humidity in a room are 300 K and 20% respectively. The volume of the room is 50 m3. The saturation vapour pressure at 300 K 3.3 kPa. Calculate the mass of the water vapour present in the room.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
A bucket full of water is placed in a room at 15°C with initial relative humidity 40%. The volume of the room is 50 m3. (a) How much water will evaporate? (b) If the room temperature is increased by 5°C, how much more water will evaporate? The saturation vapour pressure of water at 15°C and 20°C are 1.6 kPa and 2.4 kPa respectively.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
If 1022 gas molecules each of mass 10-26 kg collide with a surface (perpendicular to it) elastically per second over an area of 1 m2 with a speed of 104 m/s, the pressure exerted by the gas molecules will be of the order of ______.
In a cubical box of volume V, there are N molecules of a gas moving randomly. If m is mass of each molecule and v2 is the mean square of x component of the velocity of molecules, then the pressure of the gas is ______.
