Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State any four properties of progressive wave.
Solution
The properties of progressive waves are:
Amplitude, wavelength, period, double periodicity, frequency and velocity.
Progressive waves are classified into two types:
- Transverse progressive waves
- Longitudinal progressive waves
Characteristics of progressive waves:
- All the vibrating particles of the medium have the same amplitude, period, and frequency.
- State of oscillation, i.e., phase changes from particle to particle.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer briefly.
Wave motion is doubly periodic. Explain.
Answer briefly.
Draw a wave and indicate points which are
- in phase
- out of phase
- have a phase difference of `pi/2`
Answer briefly.
Define the relation between velocity, wavelength and frequency of the wave.
Solve the following problem.
A certain sound wave in air has a speed 340 m/s and wavelength 1.7 m for this wave, calculate
- the frequency
- the period
Solve the following problem.
A tuning fork of frequency 170 Hz produces sound waves of wavelength 2 m. Calculate the speed of sound.
Sound wave A has period 0.015 s, sound wave B has a period of 0.025 s. Which sound has greater frequency?
Two sinusoidal plane waves of the same frequency having intensities I0 and 4I0 are travelling in the same direction. The resultant intensity at a point at which waves meet with a phase difference of zero radians is ______
Two waves of the same amplitude superimpose to produce two beats per second. What is the ratio of minimum loudness to that of one of the waves?
The ratio of minimum to maximum wavelength in Balmer series is ____________.
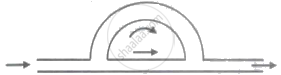
Sound waves are passing through two routes one in straight path and the other along a semicircular path of radius r and are again combined into one pipe and superposed as shown in the figure. If the velocity of sound waves in the pipe is v, then frequencies of resultant waves of maximum amplitude will be integral multiples of ______.
In frequency modulated wave ______.
The frequency of a tuning fork is 384 per second and velocity of sound in air is 352 m/s. How far the sound has traversed while fork completes 48 vibration?
The wave of the wavelength 30 cm and frequency 100 Hz will be ______.
When the kinetic energy of an electron is increased, the wavelength of the associated wave will ______.
A progressive wave of frequency 50 Hz is travelling with velocity 350 m/s through a medium. The change in phase at a given time interval of 0.01 s is ______.
When the observer moves towards a stationary source with velocity V1, the apparent frequency of emitted note is F1. When observer moves away from the source with velocity V1, the apparent frequency is F2. If V is the velocity of sound in air and `"F"_1/"F"_2=2` then `"V"/"V"_1` is equal to ______.
The equation of wave motion is `y = 6 sin[12pit-0.02pix+pi/2],` where x is in m and t in second. The velocity of the wave is ______.
The width of a slit is 0.012 mm. Monochromatic light is incident on it. The angular position of first bright line is 5.2°. The wavelength of incident light is ______. [sin 5.2° = 0.0906].
In communication system, the process of superimposing a low frequency signal on a high frequency wave is known as ______.
If a string fixed at both ends vibrates in four loops. The wavelength is 10 cm. The length of string is ______.
The energy of photon corresponding to a radiation of wavelength 600 nm is 3.32 × 10−19 J. The energy of a photon corresponding to a wavelength of 400 nm is ______.
