Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State Newton's law of gravitation. What is the difference between:
Gravity and gravitation
Solution
Newton law of gravitation is that every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Gravity is the force of attraction between the object and the earth whereas gravitation refers to the force of attraction that exists between any two bodies that possess mass.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Calculate the force of gravitation between the earth and the Sun, given that the mass of the earth = 6 × 1024 kg and of the Sun = 2 × 1030 kg. The average distance between the two is 1.5 × 1011 m.
Consider a planet moving in an elliptical orbit round the sun. The work done on the planet by the gravitational force of the sun
(a) is zero in any small part of the orbit
(b) is zero in some parts of the orbit
(c) is zero in one complete revolution
(d) is zero in no part of the motion.
Two spherical balls of mass 10 kg each are placed 10 cm apart. Find the gravitational force of attraction between them.
Multiple Choice Question. Select the correct option.
The mass of earth is 6 × 1024 kg and radius of earth is 6.4 × 106 m. The magnitude of force between the mass of 1 kg and the earth is:
An apple falls towards the earth due to its gravitational force. The apple also attracts the earth with the same force. Why do we not see the earth rising towards the apple? Explain.
Particles of masses 2M, m and M are respectively at points A, B and C with AB = ½ (BC). m is much-much smaller than M and at time t = 0, they are all at rest (Figure). At subsequent times before any collision takes place ______.

Shown are several curves (Figure). Explain with reason, which ones amongst them can be possible trajectories traced by a projectile (neglect air friction).
Answer the following questions in reference to the figure below:
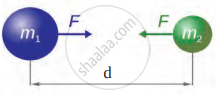
- Which relation is shown in the figure?
- What will happen if the mass of one of the objects is doubled?
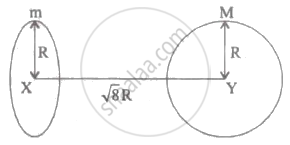
Find the gravitational force of attraction between the ring and sphere as shown in the diagram, where the plane of the ring is perpendicular to the line joining the centres. If `sqrt8` R is the distance between the centres of a ring (of mass 'm')and a sphere (mass 'M') where both have equal radius 'R'.
Newton's universal law of gravitation applies to ______.
