Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The distance between Delhi and Agra is 200 km. A train travels the first 100 km at a speed of 50 km/h. How fast must the train travel the next 100 km, so as to average 70 km/h for the whole journey ?
Solution
We have the following data to find the speed for the second part of the journey:
Total distance to be travelled by train (D) = 200 km
Average speed required (vavg) = 70 km/hr
Time required for the entire journey (T) :
`"Time" = "Total Distance"/"Average speed"`
= `200/70` hr
T = `20/7` hr
For the first part of the trip:
Distance covered (d1) = 100 km
Speed for this part of journey (v1) = 50 km/hr
Time taken for the first part of journey :
`"Time" = "Distance travelled"/"Speed"`
So,
t1 = `100/50` hr
= 2 hr
For the second part of the trip,
Distance covered (d2) = 100 km
Time taken for the second part of journey :
t2 = T-t1
= `(20/7 - 2)` hr
= `6/7` hr
Speed of the train for the second part of the journey :
= `"distance travelled"/"Time"`
= `((100)(7))/6`
= 116.67 km/hr
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Change the speed of 6 m/s into km/h.
An aircraft travelling at 600 km/h accelerates steadily at 10 km/h per second. Taking the speed of sound as 1100 km/h at the aircraft’s altitude, how long will it take to reach the ‘sound barrier’ ?
Convert a speed of 54 km/h into m/s.
A car travels 100 km at a speed of 60 km/h and returns with a speed of 40 km/h. Calculate the average speed for the whole journey.
Give one example of following motion :
Uniform velocity
A car accelerates at a rate of 5 m s-2. Find the increase in its velocity in 2 s.
The velocity-time graph of a moving body is given below in Figure
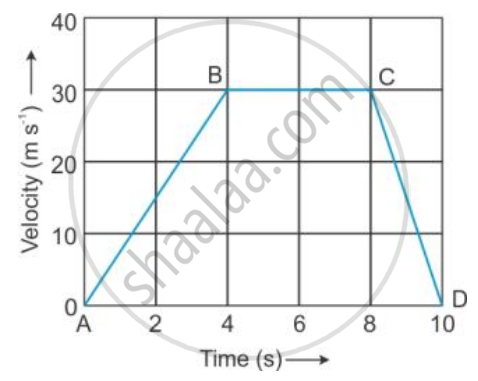
The acceleration in parts AB, BC and CD.
A speeding car changes its velocity from 108 kmh−1 to 36 kmh−1 in 4 s. Calculate its deceleration in
- ms−2
- kmh−2.
How many variables are present in each equation of motion?
