Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A car accelerates at a rate of 5 m s-2. Find the increase in its velocity in 2 s.
Solution
Acceleration = Increase in velocity/time taken
Therefore, increase in velocity = Acceleration × time taken
= (5 × 2) m/s
= 10 m/s
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A snail covers a distance of 100 metres in 50 hours. Calculate the average speed of snail in km/h.



A ball hits a wall horizontally at 6.0 m s-1. It rebounds horizontally at 4.4 m s-1. The ball is in contact with the wall for 0.040 s. What is the acceleration of the ball ?
The tip of seconds’ hand of a dock takes 60 seconds to move once on the circular dial of the clock. If the radius of the dial of the clock be 10.5 cm, calculate the speed of the tip of the seconds’ hand of the clock. `("Given" π= 22/7)`.
The graph given alongside shows how the speed of a car changes with time:

(i) What is the initial speed of the car ?
(ii) What is the maximum speed attained by the car ?
(iii) Which part of the graph shows zero acceleration ?
(iv) Which part of the graph shows varying retardation ?
(v) Find the distance travelled in first 8 hours.
What do you mean by motion in one direction?
Give one example of following motion :
Variable velocity
Draw the shape of the velocity-time graph for a body moving with (a) Uniform velocity and (b) Uniform acceleration.
The velocity-time graph of a moving body is given below in Figure
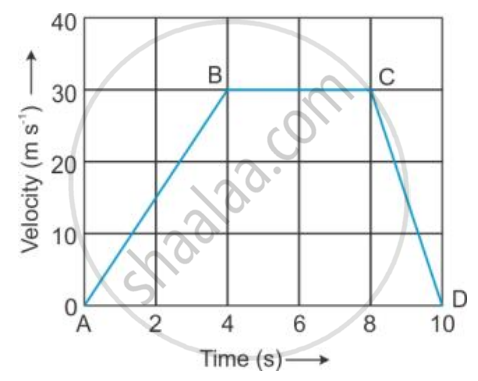
Displacement in each part AB, BC and CD.
A speeding car changes its velocity from 108 kmh−1 to 36 kmh−1 in 4 s. Calculate its deceleration in
- ms−2
- kmh−2.
How many variables are present in each equation of motion?
