Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The velocity-time graph of a moving body is given below in Figure
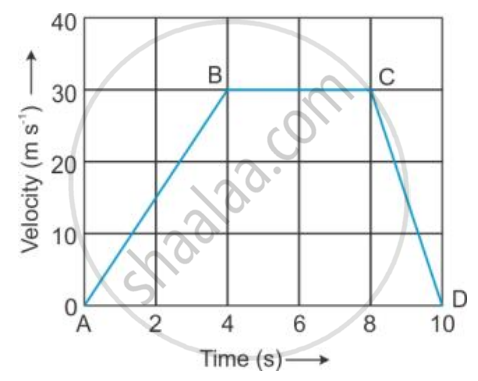
Displacement in each part AB, BC and CD.
Solution
Displacement of part AB = Area of ΔAB4 = (1/2) (4) (30)
= 60 m
Displacement of part BC = Area of rectangle 4BC8
= (30) × (4) = 120 m
Displacement of part CD = Area of ΔC8D = (1/2) (2) (30)
= 30 m
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An aircraft travelling at 600 km/h accelerates steadily at 10 km/h per second. Taking the speed of sound as 1100 km/h at the aircraft’s altitude, how long will it take to reach the ‘sound barrier’ ?
A ball hits a wall horizontally at 6.0 m s-1. It rebounds horizontally at 4.4 m s-1. The ball is in contact with the wall for 0.040 s. What is the acceleration of the ball ?
One of the following is not a vector quantity. This one is :
Give one example of following motion :
Variable velocity
A car is moving with a velocity 20 m s-1. The brakes are applied to retard it at a rate of 2 m s-2. What will be the velocity after 5 s of applying the brakes?
From the displacement-time graph of a cyclist given below in the Figure, find The average velocity in the first 4 s.

The velocity-time graph of a moving body is given below in Figure
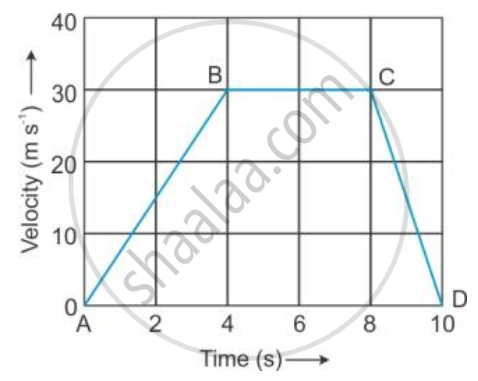
Total displacement.
A train is moving with a velocity of 90 km h-1 . It is brought to stop by applying the brakes which produce a retardation of 0.5 ms-2 Find :
(i) The velocity after 10 s , and
(ii) the time taken by the train to come to rest .
What is the relation between distance and time when the body is moving with variable velocity?
Which of the following figures (Fig. 8.3) represents uniform motion of a moving object correctly?
