Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A car is moving with a velocity 20 m s-1. The brakes are applied to retard it at a rate of 2 m s-2. What will be the velocity after 5 s of applying the brakes?
Solution
Initial velocity of the car, u = 20 m/s
Retardation = 2 m/s2
Given time, t = 5 s
Let 'v' be the final velocity.
We know that, Acceleration = Rate of change of velocity/time
= (Final velocity - Initial velocity)/time
⇒ - 2 = `("v" - 20)/5`
⇒ - 2 × 5 = v - 20
⇒ - 10 = v - 20
⇒ - 10 + 20 = v
⇒ v = 10 m/s
Hence, final velocity = 10 m s-1.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name the physical quantity obtained by dividing ‘Distance travelled’ by ‘Time taken’ to travel that distance.
A motorcyclist drives from place A to B with a uniform speed of 30 km h-1 and returns from place B to A with a uniform speed of 20 km h-1. Find his average speed.
If a bus travelling at 20 m/s is subjected to a steady deceleration of 5 m/s2, how long will it take to come to rest ?
Give one example of a motion where an object does not change its speed but its direction of motion changes continuously.
The graph given alongside shows how the speed of a car changes with time:

(i) What is the initial speed of the car ?
(ii) What is the maximum speed attained by the car ?
(iii) Which part of the graph shows zero acceleration ?
(iv) Which part of the graph shows varying retardation ?
(v) Find the distance travelled in first 8 hours.
Define variable velocity and give one example.
What is the relation between distance and time when the body is moving with uniform velocity?
A speeding car changes its velocity from 108 kmh−1 to 36 kmh−1 in 4 s. Calculate its deceleration in
- ms−2
- kmh−2.
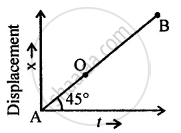
Write down the type of motion of a body along with the A – O – B of the following distance – time graph.
Give two examples of uniform circular motion from your daily life.
