Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If a bus travelling at 20 m/s is subjected to a steady deceleration of 5 m/s2, how long will it take to come to rest ?
Solution
We have to find the time taken to reach the given final velocity.
We have:
Initial velocity (u) = 20 m/s
Final velocity (v) = 0 m/s
Acceleration for the entire journey (a) = –5 ms2.
Let the time taken be (t).
We can calculate the time taken using the first equation of motion.
`t = (v-u)/a`
Time taken by the bus to come to rest:
= `(0-20)/-5`
= 4 s
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What name is given to the speed in a specified direction ?
A train starting from Railway Station attains a speed of 21 m/s in one minute. Find its acceleration.
A train travels the first 15 km at a uniform speed of 30 km/h; the next 75 km at a uniform speed of 50 km/h; and the last 10 km at a uniform speed of 20 km/h. Calculate the average speed for the entire train journey.
Give an example of motion in which the average speed is not zero but the average velocity is zero.
Which of the quantity-velocity or acceleration-determines the direction of motion?
Express 15 m s-1 in km h-1.
A car is moving in a straight line with speed 18 km h-1. It is stopped in 5 s by applying the brakes. Find:
- the speed of car in m s-1
- the retardation and
- the speed of car after 2 s of applying the brakes.
From the displacement-time graph of a cyclist given below in the Figure, find The average velocity in the first 4 s.

The velocity-time graph of a moving body is given below in Figure
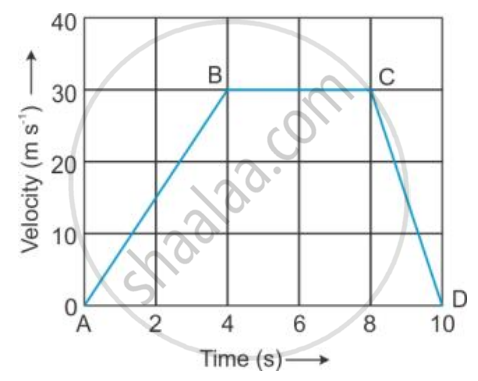
Displacement in each part AB, BC and CD.
A train is moving with a velocity of 90 km h-1 . It is brought to stop by applying the brakes which produce a retardation of 0.5 ms-2 Find :
(i) The velocity after 10 s , and
(ii) the time taken by the train to come to rest .
