Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The energy contained in a small volume through which an electromagnetic wave is passing oscillates with
Options
zero frequency
the frequency of the wave
half the frequency of the wave
double the frequency of the wave
Solution
double the frequency of the wave
The energy per unit volume of an electromagnetic wave,
`u = 1/2 ∈_0 E^2 + B^2/(2u_0)`
The energy of the given volume can be calculated by multiplying the volume with the above expression.
`U = u xx V = (1/2 ∈_0 E^2 + B^2/(2u_0)) xx V` ...(1)
Let the direction of propagation of the electromagnetic wave be along the z-axis. Then, the electric and magnetic fields at a particular point are given by
Ex= E0 sin (kz – ωt)
By= B0 sin (kz – ωt)
Substituting the values of electric and magnetic fields in (1), we get :
`U = (1/2 ∈_0 (E_0^2 sin^2(kz - ωt) + (B_0^2sin^2(kz – ωt))/(2u_0)) xx V`
⇒ `U = (∈_0 E_0^2 ((1-cos(2kz - 2ωt)))/4 + (B_0^2(1-cos(2kz-2ωt)))/(4u_0)) xx V`
From the above expression, it can be easily understood that the energy of the electric and magnetic fields have angular frequency 2ω. Thus, the frequency of the energy of the electromagnetic wave will also be double.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How are electromagnetic waves produced?
Draw a schematic sketch of the electromagnetic waves propagating along the + x-axis. Indicate the directions of the electric and magnetic fields
A charged particle oscillates about its mean equilibrium position with a frequency of 109 Hz. What is the frequency of the electromagnetic waves produced by the oscillator?
How is the speed of em-waves in vacuum determined by the electric and magnetic field?
What are the directions of electric and magnetic field vectors relative to each other and relative to the direction of propagation of electromagnetic waves?
A capacitor is connected to an alternating-current source. Is there a magnetic field between the plates?
The electric and magnetic fields, associated with an electromagnetic wave, propagating along negative X-axis can be represented by ______.
If the magnetic monopole exists, then which of the Maxwell’s equation to be modified?
The electric and magnetic fields of an electromagnetic wave are ______.
Write a short note on the microwave.
Discuss the source of electromagnetic waves.
A pulse of light of duration 10-6 s is absorbed completely by a small object initially at rest. If the power of the pulse is 60 x 10-3 W, calculate the final momentum of the object.
A plane electromagnetic wave propagating along x direction can have the following pairs of E and B.
- Ex, By.
- Ey, Bz.
- Bx, Ey.
- Ex, By.
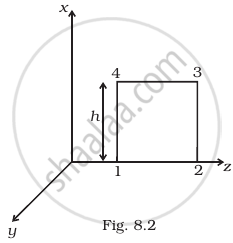
A plane EM wave travelling in vacuum along z direction is given by `E = E_0 sin(kz - ωt)hati` and `B = B_0 sin(kz - ωt)hatj`
- Evaluate `oint E.dl` over the rectangular loop 1234 shown in figure.
- Evaluate `int B.ds` over the surface bounded by loop 1234.
- Use equation `oint E.dl = (-dphi_B)/(dt)` to prove `E_0/B_0` = c.
- By using similar process and the equation `ointB.dl = mu_0I + ε_0 (dphi_E)/(dt)`, prove that c = `1/sqrt(mu_0ε_0)`
A plane electromagnetic wave travels in free space along the x-direction. The electric field component of the wave at a particular point of space and time is E = 6 Vm-1 along the y-direction. Its corresponding magnetic field component, B would be ______.
The electric field in an electromagnetic wave is given by E = 56.5 sin ω(t - x/c)Nc-1. Find the intensity of the wave if it is propagating along x-axis in the free space.
(Given ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2 N-1 m-2)
A 27 mW laser beam has a cross-sectional area of 10 mm2. The magnitude of the maximum electric field in this electromagnetic wave is given by:
[Given permittivity of space ∈0 = 9 × 10-12 SI units, Speed of light c = 3 108 m/s]
An electromagnetic wave is produced by a charge ______.
Name the electromagnetic wave/radiation which is used to study crystal structure.
