Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The free surface of oil in a tanker, at rest, is horizontal. If the tanker starts accelerating the free surface will be titled by an angle θ. If the acceleration is a ms–2, what will be the slope of the free surface?
Solution
The behaviour of a liquid contained in a horizontally accelerated vessel can be understood by understanding the behaviour of a pendulum suspended from the ceiling of a horizontally accelerated trolley.
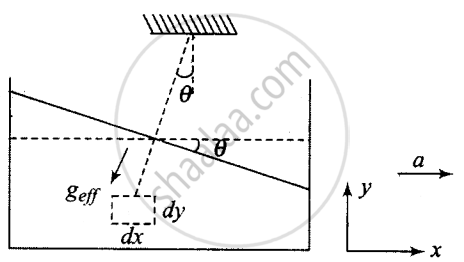
Every fluid element attains an equilibrium position under the action of gravity and pseudo-force. The free surface of the liquid orients itself perpendicular to the direction of net effective gravity.
tan θ = a/g
Suppose a tanker accelerates along the x-axis with acceleration a, the free surface of the tanker will not be horizontal because pseudo force acts as shown in the diagram.
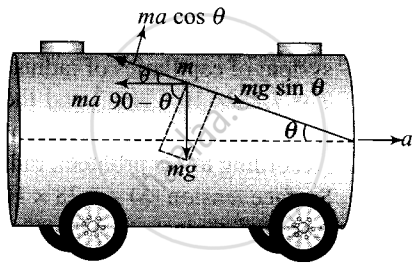
Consider an elementary particle of the oil of mass m.
The acting forces on the particle with respect to the tanker are shown in the figure alongside.
Now, balancing forces (as the particle is in equilibrium) along the inclined direction of the surface.
ma = pseudo force
mg = weight of small part of the oil.
Along the free surface,
Net force = 0
⇒ ma cos θ = mg sin θ
⇒ a = g tan θ
⇒ θ = tan-1(a/g)
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A U-shaped wire is dipped in a soap solution and removed. The thin soap film formed between the wire and the light slider supports a weight of 1.5 × 10–2 N (which includes the small weight of the slider). The length of the slider is 30 cm. What is the surface tension of the film?
The free surface of a liquid resting in an inertial frame is horizontal. Does the normal to the free surface pass through the centre of the earth? Think separately if the liquid is (a) at the equator (b) at a pole (c) somewhere else.
A 20 cm long capillary tube is dipped in water. The water rises up to 8 cm. If the entire arrangement is put in a freely falling elevator, the length of water column in the capillary tube will be
Find the force exerted by the water on a 2 m2 plane surface of a large stone placed at the bottom of a sea 500 m deep. Does the force depend on the orientation of the surface?
A cube of ice floats partly in water and partly in K.oil (in the following figure). Find the ratio of the volume of ice immersed in water to that in K.oil. Specific gravity of K.oil is 0.8 and that of ice is 0.9.

A drop of mercury of radius 0.2 cm is broken into 8 droplets of the same size. Find the work done if the surface tension of mercury is 435.5 dyn/cm.
Insect moves over the surface of water because of ______.
A molecule of water on the surface experiences a net ______.
When an air bubble of radius r rises from the bottom to the surface of a lake, its radius becomes `(5r)/4`. Taking the atmospheric pressure to be equal to the 10 m height of the water column, the depth of the lake would approximately be ______.
(ignore the surface tension and the effect of temperature)
Find the work done when a drop of mercury of radius 2 mm breaks into 8 equal droplets. [Surface tension of mercury = 0.4855 J/m2].
