Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Read each statement below carefully, and state, with reasons, if it is true or false;
The instantaneous acceleration of the point of contact during rolling is zero.
Solution
False
When a body is rolling, its instantaneous acceleration is not equal to zero. It has some value.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Read each statement below carefully, and state, with reasons, if it is true or false;
During rolling, the force of friction acts in the same direction as the direction of motion of the CM of the body
To accelerate a car we ignite petrol in the engine of the car. Since only an external force can accelerate the centre of mass, is it proper to say that "the force generated by the engine accelerates the car"?
A ball is moved on a horizontal table with some velocity. The ball stops after moving some distance. Which external force is responsible for the change in the momentum of the ball?
Two blocks of masses 10 kg and 20 kg are placed on the X-axis. The first mass is moved on the axis by a distance of 2 cm. By what distance should the second mass be moved to keep the position of the centre of mass unchanged?
When a fat person tries to touch his toes, keeping the legs straight, he generally falls. Explain with reference to the following figure.
Solve the previous problem if the coefficient of restitution is e. \[\text{ Use } \theta = 45^\circ\, e = \frac{3}{4} \text{ and h = 5 m } .\]
A ball falls on an inclined plane of inclination θ from a height h above the point of impact and makes a perfectly elastic collision. Where will it hit the plane again?
Three identical spheres, each of mass M, are placed at the comers of a right angle triangle with mutually perpendicular sides equal to 2 m (see figure). Taking the point of intersection of the two mutually perpendicular sides as the origin, find the position vector of centre of mass.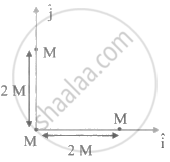
Two objects of masses 300 g and 700 g possess velocities `15 hat"i"` m/s and `4 hat"i" + 6 hat"j"` m/s respectively. The velocity of their centre of mass in m/s is:
If the net external force acting on the system of particles is zero, then which of the following may vary?
