Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The mature sperms are stored in the ____________.
Options
Seminiferous tubules
Vas deferens
Epididymis
Seminal vesicle
Solution
The mature sperms are stored in the Epididymis.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Describe, in brief, the changes the uterus undergoes
(i) to receive the zygote.
(ii) if zygote is not formed
What is placenta?
State its functions in case of a pregnant human female.
Describe in brief what happens to the zygote after it gets implanted.
The diagram given below is that of a developing human foetus. Study the diagram and then answer the questions that follow:

(i) Label the parts numbered 1 to 3 in the diagram.
(ii) Mention any two functions of the part labelled 2 in the diagram.
(iii) Explain the significance of the part numbered 3 in the diagram.
(iv) Define the term ‘Gestation’. What is the normal gestational period of the developing human embryo?
(v) Mention the sex chromosomes in a male and female embryo.
Which structure in human female is equivalent to the testes in the male?and in what respect the structures are equivalent?
When a fertilised egg E formed in the oviduct of a human female divides repeatedly to form an embryo, the embryo gets implanted in the thick and soft lining of the uterus. After this a disc-like special tissue T develops between the uterus wall and embryo through which all the requirements of the developing embryo (and foetus) are met from the mother's body, The embryo is connected to the tissue T through a string like structure S.
(a) What is the other name of fertilised egg cell E?
(b) What is the name of tissue T?
(c) Name the string-like structure S.
(d) Name two substances which pass from mother's blood to embryo through tissue T and, one type of substance which passes from embryo to mother's blood.
(e) What happens to S when the baby is born? Why?
Explain how the transmission of virus and bacteria diseases be prevented?
State the role of placenta in the development of embryo.
The vagina is a muscular tube.
Choose the correct answer:
When pregnancy does not occur, the life of corpus luteum is about _____________
Name the following:
Organ where implantation takes place.
Define the following:
Asexual reproduction
Define the following:
Clone
Define the four stages in the uterine cycle.
The following is the illustration of the sequence of ovarian events (a-i) in a human female.
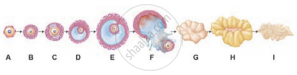
Write the difference between C and H.
Freshly released human egg has ______.
Human eggs are______.
The living organisms can be unexceptionally distinguished from the non-living things on the basis of their ability for ______.
Mention any two changes that are common to both boys and girls in early teenage years.
