Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The mutual inductance M12 of coil 1 with respect to coil 2 ______.
- increases when they are brought nearer.
- depends on the current passing through the coils.
- increases when one of them is rotated about an axis.
- is the same as M21 of coil 2 with respect to coil 1.
Options
a and b
b and c
c and d
a and d
Solution
a and d
Explanation:
Mutual Induction: Whenever the current passing through a coil or circuit changes, the magnetic flux linked with a neighbouring coil or circuit will also change. Hence an emf will be induced in the neighbouring coil or circuit. This phenomenon is called ‘mutual induction’.
The mutual inductance M12 of coil 1 w.r.t. coil 2 increases when they are brought nearer and is the same as M21 of coil 2 with respect to coil 1.
M12, i.e., mutual inductance of solenoid S1 with respect to solenoid S2 is given by
`M_12 = (mu_0N_1N_2pir_1^2)/l`
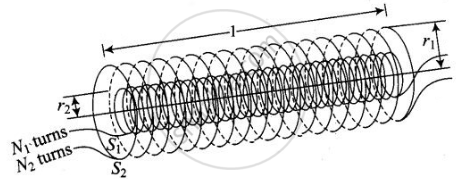
Where signs are as usual.
Also, M21, i.e., mutual inductance of solenoid S2 with respect to solenoid S1 is given by
`M_21 = (mu_0N_1N_2pir_1^2)/l`
So, we have M12 = M21 = M
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a necessary arrangement for winding of primary and secondary coils in a step-up transformer. State its underlying principle and derive the relation between the primary and secondary voltages in terms of number of primary and secondary turns. Mention the two basic assumptions used in obtaining the above relation.
A long solenoid with 15 turns per cm has a small loop of area 2.0 cm2 placed inside the solenoid normal to its axis. If the current carried by the solenoid changes steadily from 2.0 A to 4.0 A in 0.1 s, what is the induced emf in the loop while the current is changing?
A 1.0 m long metallic rod is rotated with an angular frequency of 400 rad s−1 about an axis normal to the rod passing through its one end. The other end of the rod is in contact with a circular metallic ring. A constant and uniform magnetic field of 0.5 T parallel to the axis exists everywhere. Calculate the emf developed between the centre and the ring.
Find the mutual inductance between the circular coil and the loop shown in figure.
A solenoid of length 20 cm, area of cross-section 4.0 cm2 and having 4000 turns is placed inside another solenoid of 2000 turns having a cross-sectional area 8.0 cm2 and length 10 cm. Find the mutual inductance between the solenoids.
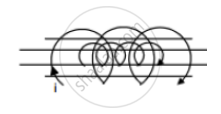
Two different wire loops are concentric and lie in the same plane. The current in the outer loop (I) is clockwise and increases with time. The induced current in the inner loop.
The mutual inductance of a pair of coils is 0.75 H. If current in the primary coil changes from 0.5 A to zero in 0.01 s, find average induced e.m.f. in secondary coil ______.
A solenoid is connected to a battery so that a steady current flows through it. If an iron core is inserted into the solenoid, the current will ______.
Two coils are placed close to each other. The mutual inductance of the pair of coils depends upon the ______.
