Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The potential difference applied across a given resistor is altered so that the heat produced per second increases by a factor of 9. By what factor does the applied potential difference change?
Solution
We know, the heat (H) produced across a resistor in time t due to flow of current (I) through it is
`H =V^2/Rt`
where, V is the potential difference applied across resistor R which gives current I.
Therefore, heat produced per second is
`H/t =V^2/R`
`⇒V^2 prop H or V prop sqrtH ` ...(i)
Now when the potential difference is altered from V to say V', then the heat produced per second increases by factor of 9
`⇒V' prop sqrt(9H)`
`or V' prop 3sqrtH` ...(ii)
Dividing (i) by (ii), we get
`(V')/V = (3sqrtH)/sqrtH`
`⇒V' = 3 V`
Hence, the potential difference changes by a factor of 3.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a labelled diagram of Van de Graaff generator. State its working principle to show how by introducing a small charged sphere into a larger sphere, a large amount of charge can be transferred to the outer sphere. State the use of this machine and also point out its limitations.
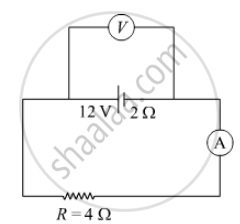
In the figure shown, an ammeter A and a resistor of 4 Ω are connected to the terminals of the source. The emf of the source is 12 V having an internal resistance of 2 Ω. Calculate the voltmeter and ammeter readings.
Draw a schematic diagram and explain the working of Van de Graff generator device.
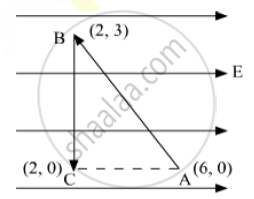
A test charge ‘q’ is moved without acceleration from A to C along the path from A to B and then from B to C in electric field E as shown in the figure. (i) Calculate the potential difference between A and C. (ii) At which point (of the two) is the electric potential more and why?
A 100 pF capacitor is charged to a potential difference of 24 V. It is connected to an uncharged capacitor of capacitance 20 pF. What will be the new potential difference across the 100 pF capacitor?
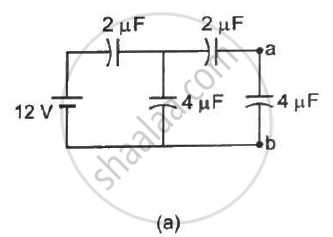
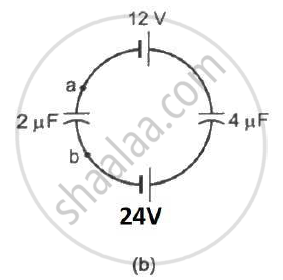
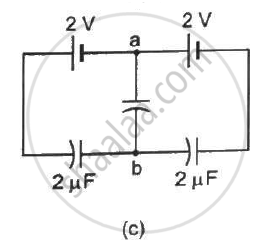
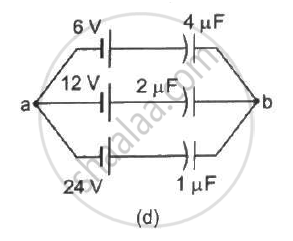
Find the potential difference `V_a - V_b` between the points a and b shown in each part of the figure.
A charge of `+2.0 xx 10^-8 C` is placed on the positive plate and a charge of `-1.0 xx 10^-8 C` on the negative plate of a parallel-plate capacitor of capacitance `1.2 xx 10^-3 "uF"` . Calculate the potential difference developed between the plates.
A charge of 20 µC is placed on the positive plate of an isolated parallel-plate capacitor of capacitance 10 µF. Calculate the potential difference developed between the plates.
On moving a charge of Q coulomb by X cm, W J of work is done, then the potential difference between the points is ______.
Can there be a potential difference between two adjacent conductors carrying the same charge?
