Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The radius of a metal sphere at room temperature T is R, and the coefficient of linear expansion of the metal is α. The sphere is heated a little by a temperature ∆T so that its new temperature is T + ∆T. The increase in the volume of the sphere is approximately ______.
Options
2πRα∆T
πR2α∆T
4πR3α∆T/3
4πR3α∆T
Solution
The radius of a metal sphere at room temperature T is R, and the coefficient of linear expansion of the metal is α. The sphere is heated a little by a temperature ∆T so that its new temperature is T + ∆T. The increase in the volume of the sphere is approximately `underline(4πR^3α∆T)`.
Explanation:
Let the radius of the sphere is R. As the temperature increases the radius of the sphere increases as shown.
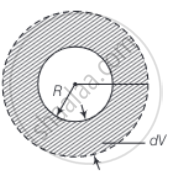
Original volume `V_0 = 4/3 piR^3`
Coefficient of linear expansion = α
∴ Coefficient of volume expansion = 3α
∴ `1/V (dV)/(dT)` = 3α
⇒ dV = 3Vαdt ≃ 4πR3α∆T
= Increase in the volume
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If two bodies are in thermal equilibrium in one frame, will they be in thermal equilibrium in all frames?
If mercury and glass had equal coefficients of volume expansion, could we make a mercury thermometer in a glass tube?
A steel rod is clamped at its two ends and rests on a fixed horizontal base. The rod is unstrained at 20°C.
Find the longitudinal strain developed in the rod if the temperature rises to 50°C. Coefficient of linear expansion of steel = 1.2 × 10–5 °C–1.
Answer the following question.
State applications of thermal expansion.
Solve the following problem.
A blacksmith fixes iron ring on the rim of the wooden wheel of a bullock cart. The diameter of the wooden rim and the iron ring are 1.5 m and 1.47 m respectively at room temperature of 27 °C. To what temperature the iron ring should be heated so that it can fit the rim of the wheel? (αiron = 1.2 × 10–5K–1).
A clock pendulum having coefficient of linear expansion. α = 9 × 10-7/°C-1 has a period of 0.5 s at 20°C. If the clock is used in a climate, where the temperature is 30°C, how much time does the clock lose in each oscillation? (g = constant)
A metal rod of cross-sectional area 3 × 10-6 m2 is suspended vertically from one end has a length 0.4 m at 100°C. Now the rod is cooled upto 0°C, but prevented from contracting by attaching a mass 'm' at the lower end. The value of 'm' is ______.
(Y = 1011 N/m2, coefficient of linear expansion = 10-5/K, g = 10m/s2)
A student records the initial length l, change in temperature ∆T and change in length ∆l of a rod as follows:
| S.No. | l(m) | ∆T (C) | ∆l (m) |
| 1. | 2 | 10 | `4 xx 10^-4` |
| 2. | 1 | 10 | `4 xx 10^-4` |
| 3. | 2 | 20 | `2 xx 10^-4` |
| 4. | 3 | 10 | `6 xx 10^-4` |
If the first observation is correct, what can you say about observations 2, 3 and 4.
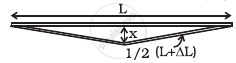
A rail track made of steel having length 10 m is clamped on a raillway line at its two ends (figure). On a summer day due to rise in temperature by 20° C, it is deformed as shown in figure. Find x (displacement of the centre) if αsteel = 1.2 × 10–5/°C.
The height of mercury column measured with brass scale at temperature T0 is H0. What height H' will the mercury column have at T = 0°C. Coefficient of volume expansion of mercury is γ. Coefficient of linear expansion of brass is α ______.
