Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The third law of Kepler is also known as the Law of ______.
Solution
The third law of Kepler is also known as the Law of Harmonies 5.8.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Let us assume that our galaxy consists of 2.5 × 1011 stars each of one solar mass. How long will a star at a distance of 50,000 ly from the galactic centre take to complete one revolution? Take the diameter of the Milky Way to be 105 ly
Identify the law shown in the figure and state three respective laws.
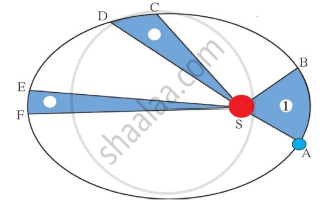
Observe the given figure showing the orbit of a planet moving around the Sun and write the three laws related to it:

The orbit of a planet moving around the Sun
The orbit of a planet revolving around a star is _______.
Observe the given figure and answer these following questions.

The orbit of a planet moving around the Sun
- What is the conclusion about the orbit of a planet?
- What is the relation between velocity of planet and distance from sun?
- Explain the relation between areas ASB, CSD and ESF.
Write the Kepler's laws.
If the distance between the sun and the earth is made three times, then attraction between the two will ______
Both earth and moon are subject to the gravitational force of the sun. As observed from the sun, the orbit of the moon ______.
If the sun and the planets carried huge amounts of opposite charges ______.
- all three of Kepler’s laws would still be valid.
- only the third law will be valid.
- the second law will not change.
- the first law will still be valid.
Supposing Newton’s law of gravitation for gravitation forces F1 and F2 between two masses m1 and m2 at positions r1 and r2 read F1 = – F2 = `- r_12/r_12^3 GM_0^2 ((m_1m_2)/M_0^2)^n` where M0 is a constant of dimension of mass r12 = r1 – r2 and n is a number. in such a case.
- the acceleration due to gravity on earth will be different for different objects.
- none of the three laws of Kepler will be valid.
- only the third law will become invalid.
- for n negative, an object lighter than water will sink in water.
