Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Two charges of magnitudes −4Q and + 2Q are located at points (2a, 0) and (5a, 0) respectively. What is the electric flux due to these charges through a sphere of radius 4a with its centre at the origin?
Solution
The sphere of radius 4a is enclosed within Only the negative charge Q1 = −4Q. Outside the sphere is the positive charge Q2 = +2Q, which is placed at a distance of 5a from the origin. Only a part of the electric flux lines originating at Q2 through the sphere and completely exit at other points. As a result, the electric flux through the sphere is solely caused by Q1.
Therefore, the net electric flux through the sphere `= "Q"_1/epsilon_0 = (-4"Q")/epsilon_0`.
Because the sphere is not centred on Q1, the minus sign indicates that the flux is directed into the sphere but not radially.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A spherical rubber balloon carries a charge, uniformly distributed over the surface. As the balloon is blown up and increases in size, the total electric flux coming out of the surface ______.
According to Gauss' theorem, the electric field of an infinitely long straight wire is proportional to ______
Gauss' law helps in ____________.
A metal sphere of radius 1 m is charged with 10-2 C in air. Its bulk modulus is `10^11/(4pi^2) "N"/"m"^2`. The volume strain in the sphere is (ε0 = permittivity of free space.)
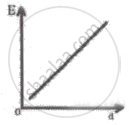
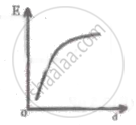
For a uniformly charged plane sheet, the variation of electric field (E) with distance (d) is correctly shown graphically in graph.
A sphere encloses an electric dipole with charges ± 3 x 10-6 C. What is the total electric flux across the sphere?
A metal sphere of radius 1 m is charged with 10-2 C in air. Its bulk modulus is 1011/4π2. The volume strain in the sphere is ______
(ε0 = permittivity of free space)
Electric field intensity at a point outside uniformly charged thin infinite plane sheet is 'E1 '. The electric field intensity at a point near and outside the surface of a positively charged conductor of any shape is 'E2'. The relation between magnitude of E1 and E2 is ______.
(assumed air as the medium)
If the radius of the spherical Gaussian surface is increased then the electric flux due to a point charge enclosed by the surface ______
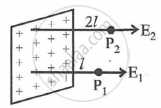
In the figure, a very large plane sheet of positive charge is shown. P1 and P2 are two points at distance l and 2l from the charge distribution. If σ is the surface charge density, then the magnitude of electric fields E1 and E2 at P1 and P2 respectively are ______.
Find the magnitude of the electric field just above the middle of a large, flat, horizontal metal sheet carrying a charge density of 90 nC/m2.
A 2-m long thin and straight metal wire carries a positive charge of 3 µ C. (a) What is the linear charge density on the wire? (b) Hence, find the electric intensity at a point 1.5 m away from the centre of the wire.
For a charged cylindrical conductor of cross-sectional radius R, what is the relation between the surface charge density and linear charge density?
What is Gauss's law?
What is a Gaussian surface?
A spherical metal ball of radius 15 cm carries a charge of 2μC. Calculate the electric field at a distance of 20 cm from the center of the sphere.