Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Two heterozygous parents are crossed. If the two loci are linked what would be the distribution of phenotypic features in F1 generation for a dihybrid cross?
Solution
Linkage is defined as the coexistence of two or more genes in the same chromosome. If the genes are situated on the same chromosome and lie close to each other, then they are inherited together and are said to be linked genes.
For example, a cross between yellow body and white eyes and wild type parent in a Drosophila will produce wild type and yellow white progenies. It is because yellow bodied and white eyed genes are linked. Therefore, they are inherited together in progenies.
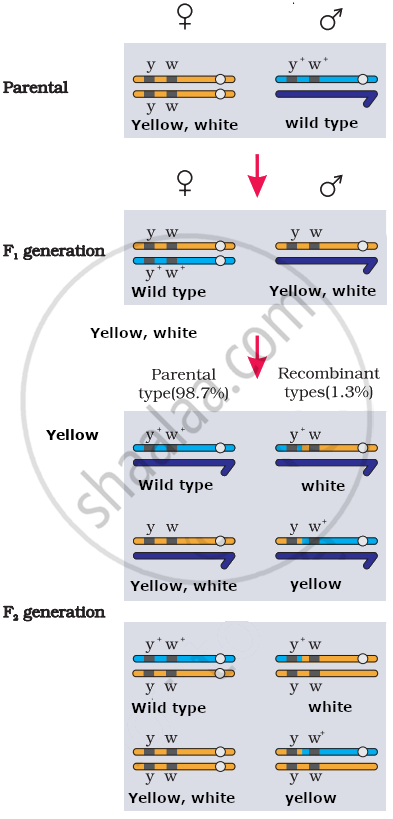
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is a dihybrid cross? How did Mendel perform this cross?
A homozygous Tall plant (T) bearing red coloured (R) flowers is crossed with a homozygous dwarf plant (t) bearing white flowers (r):
(1) Give the Genotype and Phenotype of the F2 generation.
(2) Give the possible combinations of the gametes that can be obtained from the F2 hybrid.
(3) Give the dihybrid ratio and the phenotype of the offsprings of the F2 generation when two plants of the F1 generation above are crossed.
Give Technical Term:
The ratio of offspring on F2 generation in a dihybrid cross.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
_______ is the ratio of dihybrid cross.
Complete the following sentence with appropriate word:
A character that is suppressed is _________.
Multiple Choice Question
When two individuals differing in at least one character are crossed, the process is known as:
The physical expression of a gene is called ______.
Under which conditions does the law of independent assortment hold good and why?
In pea plants, yellow seeds are dominant to green. If a heterozygous yellow seed pant is crossed with a green seeded plant, what ratio of yellow and green seeded plants would you expect in the F1 generation?
The genotype of a plant showing the dominant phenotype can be determined by
Which Mendelian idea is depicted by a cross in which the F1 generation resembles both the parents
In a test cross involving F1 dihybrid flies, more parental type offspring were produced than the recombination type offspring. This indicates
Select the period for Mendel’s hybridization experiments
Among the following characters which one was not considered by Mendel in his experimentation pea?
What is back cross?
Define Genetics.
What are the reasons for Mendel’s successes in his breeding experiment?
Identify the statementls that is/are NOT the correct reason/s for Mendel's success in his hybridization experiments.
i. Each factor controlled the single trait and is located on separate chromosomes.
ii. In the pea plant, contrasting characters can be easily recognized.
iii. Mendel carefully recorded the number of plants of each type and expressed his results as ratios.
iv. Mendel performed biochemical assays for identifying the position of 'factors' on chromosome.
Findings of Gregor Mendel were rediscovered by the following scientists EXCEPT for ______
A cross between two tall plants resulted in offspring having few dwarf plants. What would be the genotypes of both the parents?
In a dihybrid cross, if you get 9:3:3:1 ratio it denotes that ______.
In a testcross involving F1 dihybrid flies, more parental-type offspring were produced than the recombinant-type offspring. This indicates ______.
A dihybrid condition is ______.
A fruit fly exhibiting both male and female traits is ______.
In a dihybrid cross AABB x aabb, F2 progeny of AABB, AABb, AaBB and AaBb occurs in the ratio of ______.
Mendel’s Law of independent assortment holds good for genes situated on the ______.
In the F2 generation of a Mendelian dihybrid cross the number of phenotypes and genotypes are ______.
According to the evolutionary theory, formation of a new species is generally due to
Do genetic combination of mothers play a significant role in determining the sex of a new born?
Two pea plants - one with round yellow seeds (RRYY) and another with wrinkled green (rryy) seeds produce F1 progeny that have round, yellow (RrYy) seeds.
When F1 plants are self-pollinated, which new combination of characters is expected in F2 progeny? How many seeds with these new combinations of characters will be produced when a total 160 seeds are produced in F2 generation? Explain with reason.
Sahil performed an experiment to study the inheritance pattern of genes. He crossed tall pea plants (TT) with short pea plants (tt) and obtained all tall plants in F1 generation.
What will be set of genes present in the F1 generation?
Which of the following statement is not correct for two genes that show 50% recombination frequency?
In the Mendelian dihybrid cross when heterozygous round yellow is self grossed, round green offsprings are represented by the genotype.
The Law of independent assortment is applicable for the traits which ______
The ratio of 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 is due to:
