Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Two pea plants - one with round yellow seeds (RRYY) and another with wrinkled green (rryy) seeds produce F1 progeny that have round, yellow (RrYy) seeds.
When F1 plants are self-pollinated, which new combination of characters is expected in F2 progeny? How many seeds with these new combinations of characters will be produced when a total 160 seeds are produced in F2 generation? Explain with reason.
Solution
Round green : 30
Wrinkled yellow : 30
New combinations are produced because of the independent inheritance of seed shape and seed colour trait.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two heterozygous parents are crossed. If the two loci are linked what would be the distribution of phenotypic features in F1 generation for a dihybrid cross?
The physical expression of a gene is called ______.
Explain with an example the inheritance of the dihybrid cross. How is it different from monohybrid cross?
In pea plants, yellow seeds are dominant to green. If a heterozygous yellow seed pant is crossed with a green seeded plant, what ratio of yellow and green seeded plants would you expect in the F1 generation?
Define Genetics.
Findings of Gregor Mendel were rediscovered by the following scientists EXCEPT for ______
Two linked genes a and b show 20% recombination. The individuals of a dihybrid cross between ++ /++ × ab/ab shall show gametes ______.
A normal green male maize is crossed with albino female. The progeny is albino because ______.
Mendel’s last law is ______.
The process of mating between closely related individuals is ______.
In a dihybrid cross, F2 phenotypic ratio is 13 : 3. It is case of ______.
Mendel’s Law of independent assortment holds good for genes situated on the ______.
Assertion: When the two genes in a dihybrid cross are situated on the same chromosome, the proportion of parental gene combinations is much higher than the nonparental type.
Reason: Higher parental gene combinations can be attributed to crossing over between two genes.
Given below is a dihybrid cross performed on Drosophila.
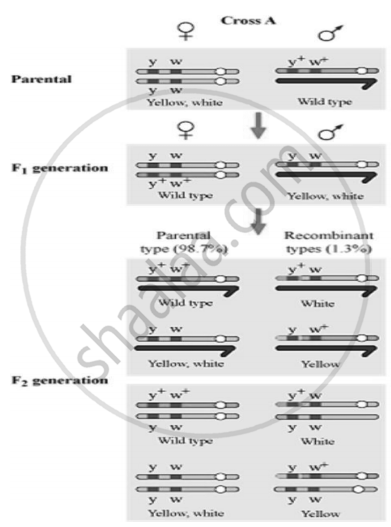
Which of the following conclusions can be drawn on the basis of this cross? When yellow bodied (y), white-eyed (w) Drosophila females were hybridized with brown bodied (y+), red-eyed males (w+) and F1 progenies were intercrossed, F2 generation would have shown the following ratio:
From the list given below, select the character which can be acquired but not inherited
Sahil performed an experiment to study the inheritance pattern of genes. He crossed tall pea plants (TT) with short pea plants (tt) and obtained all tall plants in F1 generation.
Give a reason why only tall plants are observed in F1 progeny.
Which of the following statement is not correct for two genes that show 50% recombination frequency?
When two hybrids rrTt and Rrtt are gassed, the phenotype ratio of offspring should be:
Mendel's law of independent assortment is based on F2 ratio of:
