Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Two resistors having 2Ω and 3Ω resistance are connected—(i) in series, and (ii) in parallel. Find the equivalent resistance in each case.
Solution
Given: R1 = 2 Ω, R2 = 3 Ω
(i) In series : Equivalent resistance R = R1 + R2
or R = 2 + 3 = 5 Ω
(ii) In parallel : Equivalent resistance R = `("R"_1"R"_2)/("R"_1 + "R"_2)`
or R = `(2 xx 3)/(2 + 3) = 6/5 = 1.2 Omega`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
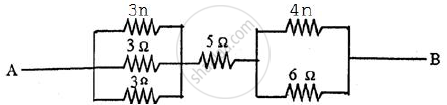
Find the equivalent resistance between points A and B
Two resistors of 4Ω and 6 Ω are connected in parallel to a cell to draw 0.5 A current from the cell.
(i) Draw a labelled circuit diagram showing the above arrangement.
(ii) Calculate the current in each resistor. What is an Ohmic resistor?
How does the presence of impurities in a metal affect its resistance?
Write down an expression for the resistance of a metallic wire in terms of the resistivity.
V = IRTwo resistances X and Y are connected turn by turn : (i) in parallel, and (ii) series. In which case the resultant resistance will be less than either of the individual resistances?R = R1+ R2+ R3
A p.d. of 4 V is applied to two resistors of 6 Ω and 2 Ω connected in series. Calculate:
(a) the combined resistance
(b) the current flowing
(c) the p.d. across the 6 Ω resistor
You have three resistors of values 2 `Omega`, 3 `Omega`, and 5 `Omega`. How will you join them so that the total resistance is less than 2 `Omega`?
State a relation between electrical power, resistance and potential difference in an electrical circuit.
Four resistances of 2.0Ω each are joined end to end, to form a square ABCD. Calculate the equivalent resistance of the combination between any two adjacent comers.
