Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Use Huygens’s principle to explain the formation of diffraction pattern due to a single slit illuminated by a monochromatic source of light.
Solution
Consider a parallel beam of monochromatic light is incident normally in a slit of width b as shown if figure. According to Huygens’s principle every point of slit acts as a source of secondary wavelets spreading in all directions. Screen is placed at a larger distance.
Consider a particular point P on the screen receives waves from all the secondary sources. All these waves start from different point of the slit and interface at point P to give
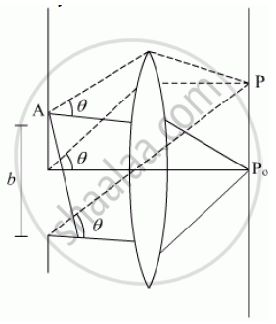
Point P0 is at bisector plane of the slit. At P0, all waves are traveling equal optical path. So are in phase the waves thus interface constructively with each other and maximum intensity is observed. As we move from P0, the wave arrives with different phase and intensity is changed. Intensity at point P is given by
`I = I_0 (sin^2α)/alpha`
where `alpha = pi/lambda b sin theta`
For central maxima α = 0 thus,
I = I0
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
On the basis of Huygens' wave theory of light prove that velocity of light in a rarer medium is greater than velocity of light in a denser medium.
The refractive indices of water and diamond are `4/3` and 2.42 respectively. Find the speed of light in water and diamond. (c = 3x108 m/s)
Using Huygens’ principle, verify the laws of reflection at a plane surface.
Answer the following question.
Define the term wavefront. Using Huygen's wave theory, verify the law of reflection.
According to Huygens principle, ______.
According to Huygen's construction, relation between old and new wavefront is ______.
Relation between ray and wavefront is ______.
What is the geometrical shape of the wavefront for:
- Light diverging from a point source?
- The pattern of wavefront of the light from a distant star intercepted by earth?
Is Huygen’s principle valid for longitudinal sound waves?
According to Huygens's principle, the amplitude of secondary wavelets is ______.
