Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Vapour pressure of pure acetone and chloroform at 328 K are 741.8 mm Hg and 632.8 mm Hg respectively. Assuming that they form ideal solution over the entire range of composition, plot `"P"_"total"`, `"P"_"chloroform"` and `"P"_"acetone"` as a function of `"x"_"acetone"`. The experimental data observed for different compositions of mixtures is:
| `bb(100 xx "x"_"acetone")` | 0 | 11.8 | 23.4 | 36.0 | 50.8 | 58.2 | 64.5 | 72.1 |
| `bb("P"_"acetone"//"mm Hg")` | 0 | 54.9 | 110.1 | 202.4 | 322.7 | 405.9 | 454.1 | 521.1 |
| `bb("P"_"chloroform"//"mm Hg")` | 632.8 | 548.1 | 469.4 | 359.7 | 257.7 | 193.6 | 161.2 | 120.7 |
Plot this data also on the same graph paper. Indicate whether it has a positive or negative deviation from the ideal solution.
Solution
| `bb(100 xx "x"_"acetone")` | 0.0 | 0.118 | 023.4 | 0.360 | 0.508 | 0.582 | 0.645 | 0.721 |
| `bb("P"_"acetone"//"mm Hg")` | 0 | 54.9 | 110.1 | 202.4 | 322.7 | 405.9 | 454.1 | 521.1 |
| `bb("P"_"chloroform"//"mm Hg")` | 632.8 | 548.1 | 469.4 | 359.7 | 257.7 | 193.6 | 161.2 | 120.7 |
| `bb("P"_"total" ("mm Hg"))` | 632.8 | 603.0 | 579.5 | 562.1 | 580.4 | 599.5 | 615.3 | 641.8 |
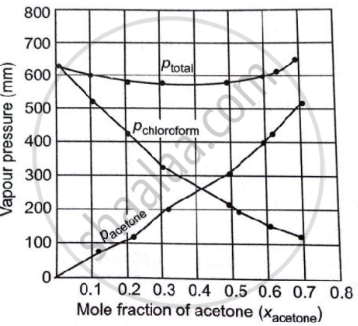
It can be observed from the graph that the plot for the ptotal of the solution curves downward. Therefore, the solution shows a negative deviation from the ideal behaviour.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What type of intermolecular attractive interaction exists in the pair of methanol and acetone?
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word/words from those given in the brackets:
Ideal solutions obey ………. law and they …………. form azeotropic mixtures.
(Henry’s, aldol condensation, absence, do not, ohm, Raoult’s, increases, common ion effect, easily, three, solubility product, ohm-1, two, four, ohm-1, cm2, Cannizzaro, ohm-1 cm-1, zero, decreases, presence)
The molality of a solution containing 1.8 g of glucose dissolved in 250 g of water is
Which one of the following is incorrect for an ideal solution?
Two liquids X and Y on mixing gives a warm solution. The solution is ______.
The mass of a non – volatile solute (molar mass 80 g mol-1) should be dissolved in 92g of toluene to reduce its vapour pressure to 90% ______.
Assertion: An ideal solution obeys Raoults Law.
Reason: In an ideal solution, solvent – solvent as well as solute – solute interactions are similar to solute-solvent interactions.
The observed depression in the freezing point of water for a particular solution is 0.093°C calculate the concentration of the solution in molality. Given that molal depression constant for water is 1.86 K Kg mol-1.
Which relationship is not correct?
Which of the following is an example of a solid solution?
Concentration terms such as mass percentage, ppm, mole fraction and molality are independent of temperature, however molarity is a function of temperature. Explain.
Explain the terms ideal and non-ideal solutions in the light of forces of interactions operating between molecules in liquid solutions.
Dissociation constant and molar conductance of an acetic acid solution are 1.78 × 10–5 mol L–1 and 48.15 S cm–2 mol–1 respectively. The conductivity of the solution is (considering molar conductance at infinite dilution is 390.5 S cm–2 mol–1)
How many times more hydrogen ions in a solution with a pH of 3 than in a solution with a pH of 6
Which of the following gave the idea of a nucleus of the atom?
While titration dilute HCl solution with aqueous NaOH, which of the following will not be required?
1 mole of liquid A and 2 moles of liquid B make a solution having a total vapour pressure of 40 torr. The vapour pressure of pure A and pure B are 45 torr and 30 torr, respectively. The above solution ______.
Suggest the most important type of intermolecular attractive interaction in the following pair.
I2 and CCl4
Suggest the most important type of intermolecular attractive interaction in the following pair.
NaClO4 and water
