Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What amount of heat must be supplied to 2.0 x 10-2 kg of nitrogen (at room temperature) to raise its temperature by 45 °C at constant pressure? (Molecular mass of N2 = 28; R = 8.3 J mol-1 K-1.)
Solution 1
Mass of nitrogen, m = 2.0 × 10–2 kg = 20 g
Rise in temperature, ΔT = 45°C
Molecular mass of N2, M = 28
Universal gas constant, R = 8.3 J mol–1 K–1
Number of moles, `n = m/M`
`= (2.0xx10^(-2)xx10^3)/28 = 0.714`
Molar specific heat at constant pressure for nitrogen, `C_P = 7/2 R`
`= 7/2 xx 8.3`
`= 29.05 J mol^(-1) K^(-1)`
The total amount of heat to be supplied is given by the relation:
ΔQ = nCP ΔT
= 0.714 × 29.05 × 45
= 933.38 J
Therefore, the amount of heat to be supplied is 933.38 J.
Solution 2
Here, mass of gas,` m= 2xx 10^-2 kg` = 20 g
rise in temperature, `triangleT = 45 ^@C`
Heat required, triangleQ = ?, Molecular mass, M = 28
Number of moles , `n = m/M = 20/28 = 0.714`
As nitrogen is a diatomatic gas,molar specific heat at constant pressure is
`C_p = 7/2R = 7/2 xx 8.3 J mol^(-1) K^(-1)`
As `triangleQ = nC_p triangleT`
`:. triangleQ = 0.714 xx 7/2 xx 8.3 xx 45 J = 933.4 J`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
You have a choice of three metals A, B, and C, of specific heat capacities 900 Jkg-1 °C-1, 380 Jkg-1 °C-1 and 460 Jkg-1 °C-1 respectively, to make a calorimeter. Which material will you select? Justify your answer.
What do you understand by the following statements:
The heat capacity of the body is 60JK-1.
What do you understand by the following statements:
The specific heat capacity of lead is 130 Jkg-1K-1.
A solid metal weighing 150 g melts at its melting point of 800 °C by providing heat at the rate of 100 W. The time taken for it to completely melt at the same temperature is 4 min. What is the specific latent heat of fusion of the metal?
During the phase change does the average kinetic energy of the molecules of the substance increase?
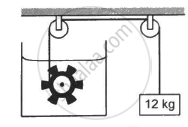
Figure shows a paddle wheel coupled to a mass of 12 kg through fixed frictionless pulleys. The paddle is immersed in a liquid of heat capacity 4200 J K−1 kept in an adiabatic container. Consider a time interval in which the 12 kg block falls slowly through 70 cm. (a) How much heat is given to the liquid? (b) How much work is done on the liquid? (c) Calculate the rise in the temperature of the liquid neglecting the heat capacity of the container and the paddle.
What is the unit of heat capacity in CGS system?
Specific heat capacity of a substance A is 3.8 J g-1 K-1 and of substance B is 0.4 J g-1 k-1. Which substance is a good conductor of heat? How did you arrive at your conclusion?
Some heat is provided to a body to raise its temperature by 25°C. What will be the corresponding rise in temperature of the body as shown on the Kelvin scale?
Write an expression for the heat energy liberated by a hot body.
63.2 g of copper at 50°C can just melt 3.8g of ice. If the specific latent heat of ice is 336 J/g, find the specific heat capacity of copper.
An electric immersion heater is rated 1250 W. Calculate the time in which it will heat 20 kg of water at 5°C to 65°C.
Read the passage and answer the questions based on it.
If heat is exchanged between a hot and cold object, the temperature of the cold object goes on increasing due to gain of energy and the temperature of the hot object goes on decreasing due to loss of energy. The change in temperature continues till the temperatures of both objects attain the same value. In this process, the cold object gains heat energy and the hot object loses heat energy. If the system of both the objects is isolated from the environment by keeping it inside a heat-resistant box then no energy can flow from inside the box or come into the box. In this situation, we get the following principle.
Heat energy lost by the hot object = Heat energy gained by the cold object. This is called the ‘Principle of heat exchange’.
- Where does heat transfer take place?
- In such a situation which principle of heat do you perceive?
- How can this principle be explained in short?
- Which property of the substance is measured using this principle?
What is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 5 kg of iron from 30°C to 130°C? Specific heat capacity of iron = 483 Jkg-1C-1.
A metal ball of heat capacity 50J/°C loses 2000 J of heat. By how much will its temperature fall?
Which of the following substances (A, B and C) has the highest specific heat?

When two kilocalories of heat are supplied to a system, the internal energy of the system increases by 5030 J and the work done by the gas against the external pressure is 3350 J. Calculate J, the mechanical equivalent of heat.
Calculate the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 200 g of copper from 20°C to 70°C. Specific heat capacity of copper = 390 J kg-1 K-1.
