Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What change is made in the eye to enable it to focus on objects situated at different distances? Illustrate your answer with the help of diagrams.
Solution

a) When the eye is focussed on a nearby object, the ciliary muscles of the eye contract, loosening the suspensory ligaments attached to the eye. As the ligaments become loose, they stop pulling the eye lens, because of which the eye lens bulges (or becomes more convex), increasing its converging power. As the converging power increases, the eye lens converges the diverging rays of light from the nearby object to form its image on the retina.
(b) When the eye is focussed on a distant object, the ciliary muscles are completely relaxed. The relaxed ciliary muscles pull the suspensory ligaments tightly. As the ligaments become tight, they pull the eye lens, because of which the eye lens becomes thinner (or less convex). The focal length of the eye lens is the maximum but its converging power is the minimum. However, the small converging power is enough to converge the parallel light rays from the distant object and form its image on the retina.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The size of the pupil becomes ______ when you see in dim light.
Match the following:
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Myopia | (a) Converging power of eye lens becomes low |
| (ii) Hypermetropia | (b) Converging power of eye lens remains the same |
| (c) Converging power of eye lens becomes high |
The optical prescription for a pair of spectacles is :
Right eye : −3.50 D
Left eye : −4.00 D
Which is the weaker eye?
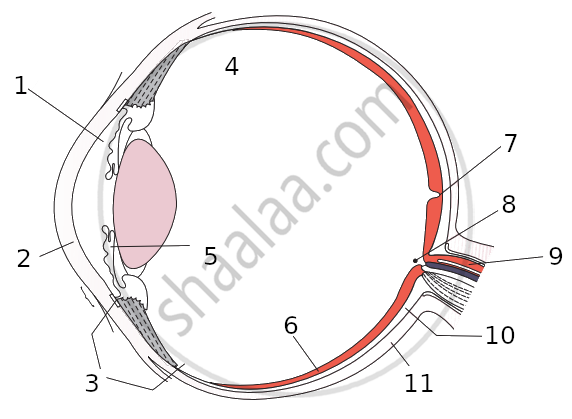
Sketch and label V.S. of a human eye.
Draw a labeled diagram of the front view of human eye.
State the Function:
Aqueous humour
Why the human eye is compared with camera?
Select the option with incorrect identification:
| Column I | Column II | ||
| 1 | Retina | a | Path way of light |
| 2 | Pupil | b | Far point comes closer |
| 3 | Ciliary muscles | c | near point moves away |
| 4 | Myopia | d | Screen of the eye |
| 5 | Hypermetropia | e | Power of accomodation |
The layer in the eye where sensory cells (rods and cones) are located ______.
