Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What does the following equation represent? Explain.
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
Solution
The given equation represents the gene frequency of the total population according to Hardy–Weinberg law. In this equation, suppose a gene has two alleles A and a, and p is the frequency of occurrence of dominant allele A and q is the frequency of occurrence of recessive allele a in the parental generation.
Then according to the equation,
p2+2pq+q2=1
where p2 = frequency of occurrence of individuals with homozygous dominant alleles (AA)
2pq = frequency of occurrence of heterozygous individuals (Aa)
q2 = frequency of occurrence of individuals with homozygous recessive alleles (aa)
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give the graphical representation of Hardy· Weinberg's principle in the form of Punnet Square.
What is the Founder's effect?
A population will not exist in Hardly Weiberg equilibrium if ____________.
How does Hardy-Weinberg’s expression (p2+2pq+q2=1) explain that genetic equilibrium is maintained in a population? List any four factors that can disturb the genetic equilibrium.
Among the five factors that are known to affect Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, three factors are gene flow, genetic drift and genetic recombination. What are the other two factors?
State and explain any three factors affecting allele frequency in populations.
"Migration may enhance or blurr the effects of selection". Comment.
The graphs below show three types of natural selection. The shaded areas marked with arrows show the individuals in the population who are not selected. The dotted vertical lines show the statistical means.
 |
 |
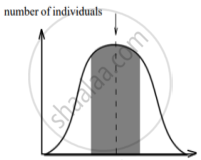 |
| character Graph A |
character Graph B |
character Graph C |
- What names are given to the types of selection shown in graphs A, B and C?
- After the selection has operated for several generations in the above populations indicated as, Graph A, B and C, graphically illustrate the probable results.
Write Hardy Weinberg's equation.
A population of 200 fruit flies is in Hardy Weinberg equilibrium. The frequency of the allele (a) 0.4. Calculate the following:
The number of homozygous dominant fruit flies.
