Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is gene therapy? Illustrate using the example of adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
Solution
Gene therapy is a genetic engineering approach that involves replacing a faulty gene with a normal, functional gene. In 1990, a 4-year-old child suffering from adenosine deaminase deficiency received the first clinical gene therapy. This enzyme is essential for the immune system to operate. Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) is caused by a gene abnormality in the enzyme adenosine deaminase. SCID patients lack functioning T-lymphocytes and cannot fight bacteria and other microorganisms.
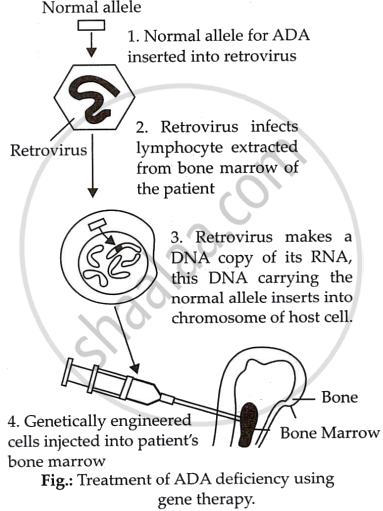
To perform gene therapy, lymphocytes are taken from the patient's bone marrow, and a normal functional copy of the human gene coding for ADA is inserted into the lymphocytes using a retroviral vector. The treated cells are reintroduced into the patient's bone marrow. These cells create lymphocytes that contain the functioning ADA gene, which reactivates the victim's immune system. However, because these lymphocytes can not divide and have a short lifespan, they must be supplied on a regular basis with engineered cells. This difficulty can be solved by modifying stem cells during the early embryonic stage.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How did an American Company, Eli Lilly use the knowledge of r-DNA technology to produce human insulin?
Recombination DNA−technology is of great importance in the field of medicine. With the help of a flow chart, show how this technology has been used in preparing genetically engineered human insulins.
Compare and contrast the advantages of production of genetically modified crops.
Expand the Given and mention one application of each:
ELISA
What is gene therapy? Name the first clinical case in which it was used.
The genetic defect adenosine deaminase deficiency may be cured permanently by ____________.
How is the amplification of a gene sample of interest carried out using PCR?
How was Insulin obtained before the advent of rDNA technology? What were the problems encountered?
PCR is a useful tool for early diagnosis of an Infectious disease. Elaborate.
ADA is an enzyme which is deficient in a genetic disorder SCID. What is the full form of ADA?
Can a disease be detected before its symptoms appear? Explain the principle involved.
Why is it that the line of treatment for a genetic disease is different from infectious diseases?
How is a mature, functional insulin hormone different from its prohormone form?
A patient is suffering from ADA deficiency. Can he be cured? How?
Name the five key tools for accomplishing the tasks of recombinant DNA technology. Also mention the functions of each tool.
A host cell must be made competent, before it is able to receive an rDNA. Justify.
- Assertion: PCR is a powerful technique to identify genetic disorders.
- Reason: PCR can detect mutations in low amounts of DNA.
The diagram given below represents the schematic structure of proinsulin, which undergoes certain modifications before it becomes a fully functional insulin.
Study the diagram carefully and answer the questions that follow:
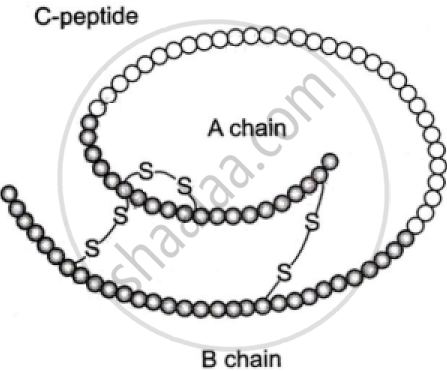
- State the change the proinsulin undergoes to become fully functional.
- Name the modern scientific technique used for the production of human insulin.
- How are the two polypeptide chains of the fully functional insulin held together?
