Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How is the amplification of a gene sample of interest carried out using PCR?
Solution
Denaturation, renaturation or primer annealing, and synthesis or primer extension, are the three steps involved in PCR. The double-stranded DNA of interest is denatured to separate into two individual strands by high temperature. This is called denaturation. Each strand is allowed to hybridize with a primer (renaturation or primer-annealing). The primer-template is used to synthesize DNA by using Taq DNA polymerase.
During denaturation, the reaction mixture is heated to 95 °C for a short time to denature the target DNA into single strands that will act as a template for DNA synthesis. Annealing is done by the rapid cooling of the mixture, allowing the primers to bind to the sequences on each of the two strands flanking the target DNA.
During primer extension or synthesis the temperature of the mixture is increased to 75°C for a sufficient period of time to allow Taq DNA polymerase to extend each primer by copying the single-stranded template. At the end of incubation, both single template strands will be made partially double-stranded. The new strand of each double-stranded DNA extends to a variable distance downstream. These steps are repeated again and again to generate multiple forms of the desired DNA. This process is also called DNA amplification.
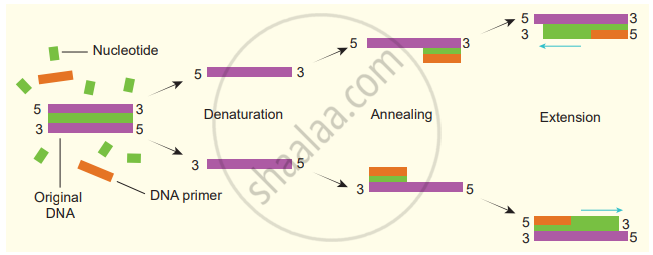
Steps involved in PCR
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the function of adenosine deaminase enzyme.
Expand the Given and mention one application of each:
PCR
Recombination DNA−technology is of great importance in the field of medicine. With the help of a flow chart, show how this technology has been used in preparing genetically engineered human insulins.
Diagrammatically represent the experimental steps in cloning and expressing an human gene (say the gene for growth hormone) into a bacterium like E. coli?
Consult internet and find out how to make orally active protein pharmaceutical. What is the major problem to be encountered?
What is gene therapy? Name the first clinical case in which it was used.
Answer the following question.
Describe the roles of heat, primers, and the bacterium Thermus aquaticus in the process of PCR.
Answer the following question.
Explain the various steps involved in the production of artificial insulin.
Describe the role of primers.
Describe the role of bacterium Thermus aquaticus in carrying the process of polymerase chain reaction.
The genetic defect adenosine deaminase deficiency may be cured permanently by ____________.
PCR proceeds in three distinct steps governed by temperature, they are in order of ____________.
If a person thinks he is infected with HIV, due to unprotected sex, and goes for a blood test. Do you think a test such as ELISA will help? If so why? If not, why?
A probe which is a molecule used to locale-specific sequences in a mixture of DNA or RNA Mole cubs could be ______.
When gene targetting involving gene amplification is attempted in an individual’s tissue to treat disease, it is known as ______
For effective treatment of the disease, early diagnosis and understanding of its pathophysiology is very important. Which of the following molecular diagnostic techniques is very useful for early detection?
Discuss briefly how a probe is used in molecular diagnostics.
Name the five key tools for accomplishing the tasks of recombinant DNA technology. Also mention the functions of each tool.
A cell-free method of amplifying DNA first developed in the mid 1980's revolutionised the field of biotechnology, Name the method and explain the basic steps of the technique involved.
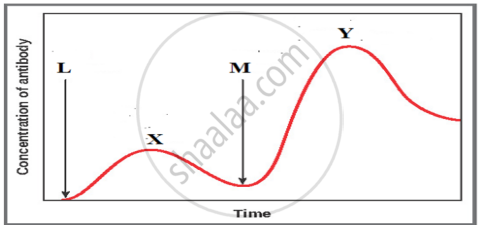
The graph given below indicates the administration of the first (L) and second dose (M) of a vaccine. The corresponding response of the body is indicated by X, and Y. Interpret the graph and explain the reason for such a response shown by the body.