Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How is the amplification of a gene sample of interest carried out using PCR?
उत्तर
Denaturation, renaturation or primer annealing, and synthesis or primer extension, are the three steps involved in PCR. The double-stranded DNA of interest is denatured to separate into two individual strands by high temperature. This is called denaturation. Each strand is allowed to hybridize with a primer (renaturation or primer-annealing). The primer-template is used to synthesize DNA by using Taq DNA polymerase.
During denaturation, the reaction mixture is heated to 95 °C for a short time to denature the target DNA into single strands that will act as a template for DNA synthesis. Annealing is done by the rapid cooling of the mixture, allowing the primers to bind to the sequences on each of the two strands flanking the target DNA.
During primer extension or synthesis the temperature of the mixture is increased to 75°C for a sufficient period of time to allow Taq DNA polymerase to extend each primer by copying the single-stranded template. At the end of incubation, both single template strands will be made partially double-stranded. The new strand of each double-stranded DNA extends to a variable distance downstream. These steps are repeated again and again to generate multiple forms of the desired DNA. This process is also called DNA amplification.
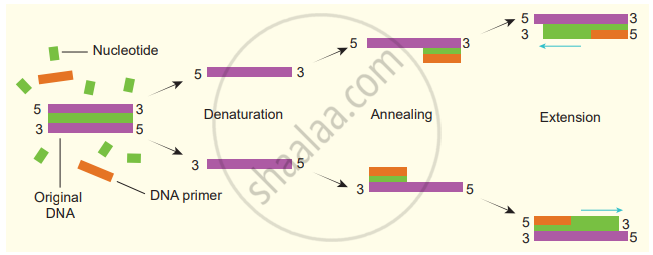
Steps involved in PCR
संबंधित प्रश्न
Suggest any two possible treatments that can be given to a patient exhibiting adenosine deaminase deficiency.
State the role of C peptide in human insulin.
Diagrammatically represent the experimental steps in cloning and expressing an human gene (say the gene for growth hormone) into a bacterium like E. coli?
Write any two biochemical/molecular diagonostic procedures for early detection of viral infection. Explain the principle of any one of them.
How many amino acids are arranged in the two chains of Insulin?
A patient suffering from diabetes mellitus will have ______.
The hormone insulin is secreted by:
Which of the following is a neuropeptide hormone?
Now a days it is possible to detect the mutated gene causing cancer by allowing a radioactive probe to hybridize its complimentary DNA in a clone of cells, followed by its detection using autoradiography because ______
Can a disease be detected before its symptoms appear? Explain the principle involved.
What is a recombinant DNA vaccine? Give two examples.
Discuss briefly how a probe is used in molecular diagnostics.
How is a mature, functional insulin hormone different from its prohormone form?
List the disadvantages of insulin obtained from the pancreas of slaughtered cows and pigs:
How does a gene therapy involving direct modification of the cells, in order to achieve a therapeutic goal is used in the treatment of ADA deficiency? Explain.
A host cell must be made competent, before it is able to receive an rDNA. Justify.
Give a reason for the following:
Streptokinase is administered to the patients having myocardial infarction.
How many cycles of PCR are required to produce 250 molecules of DNA, starting with a single parental strand?
Name the technique used to detect the presence of HIV in the body of an individual, Justify the principle associated with this technique.
