Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is lymph? Write its function.
Solution
Lymph:
About 90% of the fluid that leaks from capillaries eventually seep back into the capillaries and the remaining 10% is collected and returned to the blood system by me of a series of tubules known as lymph vessels or lymphatics.
- The fluid inside the lymphatics is called lymph. The lymphatic system consists of a complex network of thin-walled ducts (lymphatic vessels), filtering bodies (lymph nodes), and a large number of lymphocytic cell concentrations in the various lymphoid organisms.
- The lymphatic vessels have smooth walls that run parallel to the blood vessels, in the skin, along the respiratory and digestive tracts. These vessels serve as return ducts for the fluids that are continually diffusing out of the blood capillaries into the body tissues.
- Lymph fluid must pass through the lymph nodes before it is returned to the blood. The lymph nodes that filter the fluid from the lymphatic vessels of the skin are highly concentrated in the neck, inguinal, axillaries, respiratory and digestive tracts.
- The lymph fluid flowing out of the lymph nodes flows into large collecting duct which finally drains into larger veins that run beneath the collar bone, the subclavian vein, and is emptied into the blood stream. The narrow passages in the lymph nodes are the sinusoids that are lined with macrophages.
- The lymph nodes successfully prevent the invading microorganisms from reaching the blood stream. Cells found in the lymphatics are the lymphocytes. Lymphocytes collected in the lymphatic fluid are carried via the arterial blood and are recycled back to the lymph. Fats are absorbed through lymph in the lacteals present in the villi of the intestinal wall.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Which of the following is not involved in blood clotting?
Blood group is due to the presence or absence of surface ______.
A person having both antigen A and antigen B on the surface of RBCs belongs to blood group ______.
Erythroblastosis foetalis is due to the destruction of ______.
An unconscious patient is rushed into the emergency room and needs a fast blood transfusion. Because there is no time to check her medical history or determine her blood type, which type of blood should you as her doctor, give her?
Which of these functions could or could not be carried out by a red blood cell?
- Protein synthesis
- Cell division
- Lipid synthesis
- Active transport
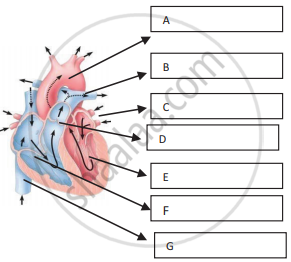
Name and Label the given diagrams to show A, B, C, D, E, F, and G
Select the correct biological term.
Disc shaped cells which are concave on both sides.
Select the correct biological term.
Most of these have a large, bilobed nucleus.
Select the correct biological term.
Enable red cells to transport blood.
Select the correct biological term.
Most of them move and change shape like an amoeba.
Select the correct biological term.
Consists of water and important dissolved substances.
Select the correct biological term.
A word that means cell eater.
Select the correct biological term.
Cells without nucleus.
Select the correct biological term.
White cells made in the lymphatic tissue.
Select the correct biological term.
Fragment of cells which are made in the bone marrow.
Select the correct biological term.
Another name for white blood cells.
