Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Kingdom Animalia
3: Tissue Level of Organisation
4: Organ and Organ Systems in Animals
5: Digestion and Absorption
6: Respiration
▶ 7: Body Fluids and Circulation
8: Excretion
9: Locomotion and Movement
10: Neural Control and Coordination
11: Chemical Coordination and Integration
12: Basic Medical Instruments and Techniques
13: Trends in Economic Zoology
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Zoology [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 7 - Body Fluids and Circulation Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Zoology [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 7 - Body Fluids and Circulation - Shaalaa.com](/images/zoology-english-class-11-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 7: Body Fluids and Circulation
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 7 of Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Samacheer Kalvi for Zoology [English] Class 11 TN Board.
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Zoology [English] Class 11 TN Board 7 Body Fluids and Circulation Evaluation [Pages 131 - 133]
What is the function of lymph?
Transport of O2 into brain
Transport of CO2 into lungs
Bring interstitial fluid in blood
Bring RBC and WBC in lymph node
Which one of the following plasma proteins is involved in the coagulation of blood?
Globulin
Fibrinogen
Albumin
Serum amylase
Which of the following is not involved in blood clotting?
Fibrin
Calcium
Platelets
Bilirubin
Lymph is colourless because ______.
WBC are absent
WBC are present
Heamoglobin is absent
RBC are absent
Blood group is due to the presence or absence of surface ______.
Antigens on the surface of WBC
Antibodies on the surface of RBC
Antigens on the surface of RBC
Antibodies on the surface of WBC
A person having both antigen A and antigen B on the surface of RBCs belongs to blood group ______.
A
B
AB
O
Erythroblastosis foetalis is due to the destruction of ______.
Foetal RBCs
Foetus suffers from atherosclerosis
Foetal WBCs
Foetus suffers from mianmata
Dub sound of heart is caused by ______.
Closure of atrio-ventricular valves
Opening of semi-lunar valves
Closure of semi-lunar values
Opening of atrio-ventricular valves.
Why is the velocity of blood flow the lowest in the capillaries?
The systemic capillaries are supplied by the left ventricle, which has a lower cardiac output than the right ventricle.
Capillaries are far from the heart, and blood flow slows as distance from the heart increases.
The total surface area of the capillaries is larger than the total surface area of the arterioles.
The capillary walls are not thin enough to allow oxygen to exchange with the cells.
The diastolic blood pressure is too low to deliver blood to the capillaries at a high flow rate.
An unconscious patient is rushed into the emergency room and needs a fast blood transfusion. Because there is no time to check her medical history or determine her blood type, which type of blood should you as her doctor, give her?
A-
AB
O+
O-
Which of these functions could or could not be carried out by a red blood cell?
Protein synthesis
Cell division
Lipid synthesis
Active transport
At the venous end of the capillary bed, the osmotic pressure is ______.
Greater than the hydrostatic pressure
Result in net outflow of fluids
Results in net absorption of fluids
No change occurs
A patient’s chart reveals that he has a cardiac output of 7500 mL per minute and a stroke volume of 50 mL. What is his pulse rate (in beats/min)
50
100
150
400
At any given time there is more blood in the venous system than that of the arterial system. Which of the following features of the veins allows this?
relative lack of smooth muscles
presence of valves
proximity of the veins to lymphatic’s
hin endothelial lining
Give any three differences between an artery and a vein
Distinguish between open circulation and closed circulation.
Distinguish between mitral valve and semi lunar valve.
Right ventricular wall is thinner than the left ventricular wall. Why?
What might be the effect on a person whose diet has less iron content?
Describe the mechanism by which the human heart beat is initiated and controlled.
What is lymph? Write its function.
What are the heart sounds? When and how are these sounds produced?
Select the correct biological term.
Disc shaped cells which are concave on both sides.
Lymphocytes
Red cells
Leucocytes
Plasma
Erythrocytes
White cells
Haemoglobin
Phagocyte
Platelets
Blood clot
Select the correct biological term.
Most of these have a large, bilobed nucleus.
Lymphocytes
Red cells
Leucocytes
Plasma
Erythrocytes
White cells
Haemoglobin
Phagocyte
Platelets
Blood clot
Select the correct biological term.
Enable red cells to transport blood.
Lymphocytes
Red cells
Leucocytes
Plasma
Erythrocytes
White cells
Haemoglobin
Phagocyte
Platelets
Blood clot
Select the correct biological term.
The liquid part of the blood.
Lymphocytes
Red cells
Leucocytes
Plasma
Erythrocytes
White cells
Haemoglobin
Phagocyte
Platelets
Blood clot
Select the correct biological term.
Most of them move and change shape like an amoeba.
Lymphocytes
Red cells
Leucocytes
Plasma
Erythrocytes
White cells
Haemoglobin
Phagocyte
Platelets
Blood clot
Select the correct biological term.
Consists of water and important dissolved substances.
Lymphocytes
Red cells
Leucocytes
Plasma
Erythrocytes
White cells
Haemoglobin
Phagocyte
Platelets
Blood clot
Select the correct biological term.
Destroyed in the liver and spleen after circulating in the blood for four months.
Lymphocytes
Red cells
Leucocytes
Plasma
Erythrocytes
White cells
Haemoglobin
Phagocyte
Platelets
Blood clot
Select the correct biological term.
The substances which gives red cells their colour.
Lymphocytes
Red cells
Leucocytes
Plasma
Erythrocytes
White cells
Haemoglobin
Phagocyte
Platelets
Blood clot
Select the correct biological term.
Another name for red blood cells.
Lymphocytes
Red cells
Leucocytes
Plasma
Erythrocytes
White cells
Haemoglobin
Phagocyte
Platelets
Blood clot
Select the correct biological term.
Blood that has been changed to a jelly
Lymphocytes
Red cells»
Lleucocytes
Plasma
Erythrocytes
White cells
Haemoglobin
Phagocyte
Platelets
Blood clot
Select the correct biological term.
A word that means cell eater.
Lymphocytes
Red cells
Leucocytes
Plasma
Erythrocytes
White cells
Haemoglobin
Phagocyte
Platelets
Blood clot
Select the correct biological term.
Cells without nucleus.
Lymphocytes
Red cells
Leucocytes
Plasma
Erythrocytes
White cells
Haemoglobin
Phagocyte
Platelets
Blood clot
Select the correct biological term.
White cells made in the lymphatic tissue.
Lymphocytes
Red cells
Leucocytes
Plasma
Erythrocytes
White cells
Haemoglobin
Phagocyte
Platelets
Blood clot
Select the correct biological term.
Blocks wound and prevent excessive bleeding.
Lymphocytes
Red cells
Leucocytes
Plasma
Erythrocytes
White cells
Haemoglobin
Phagocyte
Platelets
Blood clot
Select the correct biological term.
Fragment of cells which are made in the bone marrow.
Lymphocytes
Red cells
Leucocytes
Plasma
Erythrocytes
White cells
Haemoglobin
Phagocyte
Platelets
Blood clot
Select the correct biological term.
Another name for white blood cells.
Lymphocyte
Red cells
Leucocytes
Plasma
Erythrocytes
White cells
Haemoglobin
Phagocyte
Platelets
Blood clot
Select the correct biological term.
Slowly releases oxygen to blood cells.
Lymphocytes
Red cells
Leucocytes
Plasma
Erythrocytes
White cells
Haemoglobin
Phagocyte
Phagocyte
Blood clot
Select the correct biological term.
Their function is to help blood clot in wounds.
Lymphocytes
Red cells
Leucocytes
Plasma
Erythrocytes
White cells
Haemoglobin
Phagocyte
Platelets
Blood clot
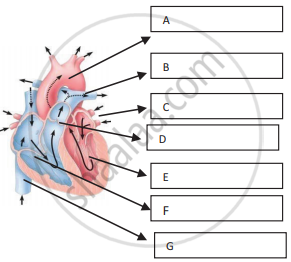
Name and Label the given diagrams to show A, B, C, D, E, F, and G
Solutions for 7: Body Fluids and Circulation
![Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Zoology [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 7 - Body Fluids and Circulation Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Zoology [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 7 - Body Fluids and Circulation - Shaalaa.com](/images/zoology-english-class-11-tn-board_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Zoology [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 7 - Body Fluids and Circulation
Shaalaa.com has the Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Mathematics Zoology [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Samacheer Kalvi solutions for Mathematics Zoology [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education 7 (Body Fluids and Circulation) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Samacheer Kalvi textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Zoology [English] Class 11 TN Board chapter 7 Body Fluids and Circulation are Body Fluids, Circulatory Pathways, Human Circulatory System, Types of Closed Circulation, Regulation of Cardiac Activity, Disorders of Circulatory System, Diagnosis and Treatment, Blood Vessels.
Using Samacheer Kalvi Zoology [English] Class 11 TN Board solutions Body Fluids and Circulation exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Samacheer Kalvi Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education Zoology [English] Class 11 TN Board students prefer Samacheer Kalvi Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 7, Body Fluids and Circulation Zoology [English] Class 11 TN Board additional questions for Mathematics Zoology [English] Class 11 TN Board Tamil Nadu Board of Secondary Education, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
