Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
Solution
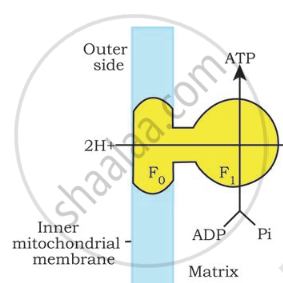
- The process of oxidative phosphorylation uses energy released during the oxidation of reduced co-enzymes (NADH, FADH2) created during respiration to synthesise energy-rich ATP molecules. ATP synthase is the name of the enzyme needed for this synthesis.
- It is regarded as the electron transport chain's fifth complex. The F1 or head component of the F0-F1 or elementary particles contains the enzyme ATP synthase.
- The inside mitochondria of the cells contain the particles. Only in situations where there is a proton gradient with a greater concentration of H+ or protons on the F0 side relative to the F1 side can ATP synthase become active in the production of ATP (the chemiosmotic theory of Peter Mitchell).
- The concentration of protons increases in the outer chamber or outer surface of the inner mitochondrial membrane as a result of protons being pushed there by energy generated during the transport of electrons from one carrier to another.
- While two pairs of protons are regularly pumped out during electron flow from FADH2, three pairs of protons are pushed to the outer chamber by the transport of electrons from NADH over ETC. The F0 channel's proton flow causes the F1 particle to act as an ATP-synthase.
- When connecting a phosphate, the energy of the proton gradient is utilised. adical via a high-energy link to ADP. ATP is created as a result. When one molecule of NADH2 is oxidised, three ATP molecules are created, whereas when FADH2 is oxidised similarly, two ATP molecules are formed.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain ETS.
Give the diagrammatic representation of ETS
Synthesis of Adenosine triphosphate during electron transfer system refers to ______.
The ultimate electron acceptor of respiration in an aerobic organisms is ______.
Match the following and choose the correct option from those given below.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Molecular oxygen | i. α - Ketoglutaric acid |
| B. Electron acceptor | ii. hydrogen acceptor |
| C. Pyruvate dehydrogenase | iii. cytochrome C |
| D. Decarboxylation | iv. acetyl Co A |
The end product of oxidative phosphorylation is ______.
Oxygen is an essential requirement for aerobic respiration but it enters the respiratory process at the end? Discuss.
Respiration is an energy releasing and enzymatically controlled catabolic process which involves a step-wise oxidative breakdown of organic substances inside living cells.
In this statement about respiration explain the meaning of 1) Step-wise oxidative breakdown, and 2) Organic substances (used as substrates).
Given below is a diagram showing ATP synthesis during aerobic respiration, replace the symbols A, B, C, D and E by appropriate terms given in the box.

F1, Particle, Pi, 2H+, Inner mitochondrial membrane, ATP, Fo particle, ADP
Oxygen is critical for aerobic respiration. Explain its role with respect to ETS.
