Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain ETS.
Solution
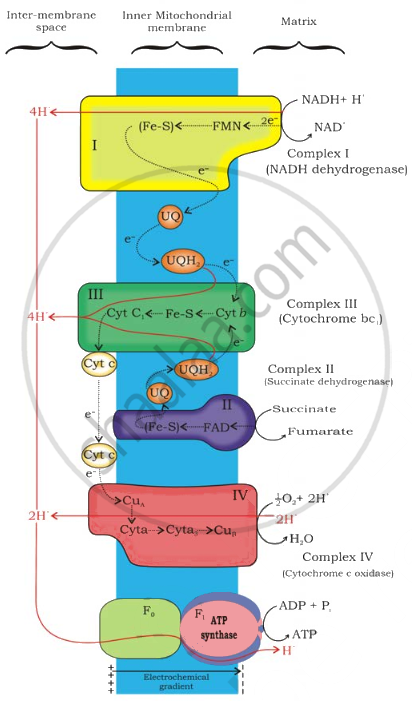
- A group of coenzymes and cytochromes that assist in moving electrons from a chemical to its final acceptor is known as an electron transport chain or system, or ETS. The electron transport chain involves reduced coenzymes.
- On the mitochondrial cristae, which are composed of oxysomes (F0-F1 particles) on the inner surface of the membrane, electron transport occurs. NADH dehydrogenase (complex I) oxidises NADH produced during the citric acid cycle and glycolysis, and the electrons are then transferred to ubiquinone. Additionally, succinate dehydrogenase (complex II) of FADH2 provides ubiquinone with reducing equivalents.
- After that, the reduced ubiquinone is oxidised through the transfer of cytochrome c electrons through the cytochrome bc1 complex (complex III). The mobile carrier that connects complex III and complex IV is cytochrome c.
- The term "Complex IV" describes the cytochrome c oxidase complex, which is made up of two copper centres, cytochromes a and a3. The electrons are connected to ATP synthetase (complex V) for the synthesis of ATP from ADP and Pi when they are transferred over the carriers via complex I to IV in the electron transport chain.
- As the final electron acceptor, oxygen is reduced to water with the help of hydrogen atoms. Reduced coenzymes, such as coenzymes I, II, and FAD, do not immediately react with molecules 0 2; instead, their hydrogen or electrons are transmitted via a variety of substances before arriving at 0 2. These compounds are known as electron carriers.
- Cytomes a and a3 together form a system known as cytochrome oxidase. Only electrons are passed by cytochromes and (Cyt b, Cyt c1, c2, a, a3) ultimately reach molecular 0. In addition to iron, Cyt a3 also contains copper.
- In order to create a water molecule, the protons that were released into the surrounding medium are now taken up by the molecular oxygen that has accepted electrons. The energy that has been released is used to create ATP from ADP and Pi.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
Give the diagrammatic representation of ETS
Synthesis of Adenosine triphosphate during electron transfer system refers to ______.
The ultimate electron acceptor of respiration in an aerobic organisms is ______.
Match the following and choose the correct option from those given below.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Molecular oxygen | i. α - Ketoglutaric acid |
| B. Electron acceptor | ii. hydrogen acceptor |
| C. Pyruvate dehydrogenase | iii. cytochrome C |
| D. Decarboxylation | iv. acetyl Co A |
The end product of oxidative phosphorylation is ______.
Oxygen is an essential requirement for aerobic respiration but it enters the respiratory process at the end? Discuss.
Respiration is an energy releasing and enzymatically controlled catabolic process which involves a step-wise oxidative breakdown of organic substances inside living cells.
In this statement about respiration explain the meaning of 1) Step-wise oxidative breakdown, and 2) Organic substances (used as substrates).
Given below is a diagram showing ATP synthesis during aerobic respiration, replace the symbols A, B, C, D and E by appropriate terms given in the box.

F1, Particle, Pi, 2H+, Inner mitochondrial membrane, ATP, Fo particle, ADP
Oxygen is critical for aerobic respiration. Explain its role with respect to ETS.
