Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is the basis for the difference in the synthesis of the leading and lagging strand of DNA molecules?
Options
Origin of replication occurs only at the 5' end of the molecules.
DNA ligase works only in the 3' → 5' direction
DNA polymerase can join new nucleotides only to the 3' end of the growing stand.
Helicases and single-strand binding proteins that work at the 5' end.
Solution
DNA polymerase can join new nucleotides only to the 3' end of the growing stand.
RELATED QUESTIONS
How CO2 makes idlies puffy?
Which enzyme does remove supercoils from replicating DNA?
Very Short Answer Question:
When does DNA replication takes place?
What is the function of SSBP?
Meselson and Stahl’s experiment proved ____________.
Differentiate - Leading stand and lagging strand.
a) Identify the figure given below
b) Redraw the structure as a replicating fork and label the parts
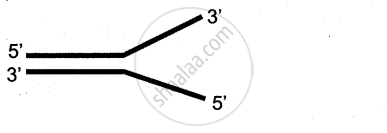
c) Write the source of energy for this replication and name the enzyme involved in this process.
d) Mention the differences in the synthesis of protein, based on the polarity of the two template strands.
Meselson and Stahl used ____________ in the experiment to prove semiconservative DNA replication.
For which of the following purpose agarose gel electrophoresis technique is used?
Which of the following technique was used by Meselson and Stahl to demonstrate the semiconservative mode of DNA replication?
Assertion (A): DNA replication is said to be semi-conservative.
Reason (R): After DNA replication, each daughter molecule has one old and one new strand.
In a segment of DNA with 10 base pairs, the numbers of sugar molecules are _________.
In DNA molecule, pairing between two complementary nucleotides takes place by ________ bonds.
Select the mis-matched pair.
"DNA is considered as genetic material" - Why?
Okazaki is known for his contribution to the under tanding of:
How many amino acids will be there in the polypeptide chain formed on the following mRNA?
5'GCCACAUGGAGAUGACGACAAAAUUUUACUAGAAAA3'
Enzyme involved in synthesis of RNA primer.
