Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is the diffraction of light? How does it differ from interference? What are Fraunhofer and Fresnel diffractions?
Solution
The phenomenon of diffraction of light:
The principle of rectilinear propagation of light from geometrical optics predicts a sharp shadow when light passes by the edge of an obstacle or through a small opening or a narrow slit and falls on a screen. However, it is discovered that some of the light deviates from its rectilinear path and enters the geometrical shadow region. This is a common feature of wave phenomena that occurs when a portion of the wavefront is obstructed in some way. This bending of light waves at an edge into the region of the geometrical shadow is called the diffraction of light.
Differences between interference and diffraction:
- Interference is the term used to describe the superposition of a few coherent waves (say, two). But when a large number of waves from different parts of the same wavefront superimpose at a point, the effect is known as diffraction.
- All double-slit interference fringes are the same width. Only the non-central maxima in a single-slit diffraction pattern are of equal width, which is half the width of the central maximum.
- The bright and dark fringes are equally spaced in double-slit interference. Only the non-central maxima in diffraction lie approximately half way between the minima.
- In double-slit interference, bright fringes are of equal intensity. In diffraction, successive noncentral maxima decrease rapidly in intensity.
Diffraction can be classified into two types depending on the distances involved in the experimental setup:
- Fraunhofer diffraction:
If the distances between the primary source of light, the obstacle/slit causing diffraction and the screen for viewing the diffraction pattern are very large, the diffraction is called Fraunhofer diffraction. In this case, the wavefront incident on the obstacle can be considered to be a plane wavefront. For this, we generally place the source of light at the focus of a convex lens so that a plane wavefront is incident on the obstacle and another convex lens is used on the other side of the obstacle to make the pattern visible on the screen.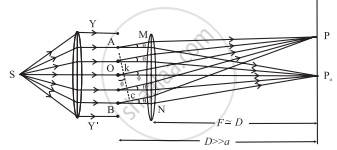
Set up for Fraunhofer diffraction - Fresnel diffraction:
In this case, the distances are much smaller and the incident wavefront is either cylindrical or spherical depending on the source. A lens is not required to observe the diffraction pattern on the screen.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The bending of a beam of light around corners of obstacle is called ______
What should be the slit width to obtain pronounced diffraction with a single slit illuminated by the light of wavelength λ?
Explain experimental setup for Fraunhofer diffraction with neat diagram.
In diffraction experiment, from a single slit, the angular width of the central maxima does not depend upon ____________.
In biprism experiment, the distance between source and eyepiece is 1.2 m, the distance between two virtual sources is 0.84 mm. Then the wavelength of light used if eyepiece is to be moved transversely through a distance of 2.799 cm to shift 30 fringes is ______.
Light of wavelength 'λ' is incident on a single slit of width 'a' and the distance between slit and screen is 'D'. In diffraction pattern, if slit width is equal to the width of the central maximum then 'D' is equal to ______.
A slit of width a is illuminated by white light. For red light `(λ = 6500 Å)`, the first minima is obtained at θ = 60°. Then the value of a will be ______.
The luminous border that surrounds the profile of a mountain just before sun rises behind it, is an example of ______.
A beam of light of wavelength 600 nm from a distant source falls on a single slit 1 mm wide and the resulting diffraction pattern is observed on a screen 4 m away. The distance between the first dark fringes on either side of the central bright fringe is ______.
For Fraunhofer diffraction to occur ____________.
In Fraunhofer diffraction pattern, slit width is 0.2 mm and screen is at 4 m away from the lens. If wavelength of light used is 5500 Å, then the distance between the first minimum on either side of the central maximum is (`theta` is small and measured in radian) ____________.
In a single slit diffraction pattern, which of the following is incorrect for fringe pattern?
The angular spread of central maximum, in diffraction pattern, does not depend on ______.
In a single slit diffraction experiment, first minimum for a light of wavelength 480 nm coincides with the first maximum of another wavelength `lambda.` Then `lambda'` is ____________.
The diffraction fringes obtained by a single slit are of ____________.
In Fresnel's biprism experiment, when the distance between the slit aperture and eye is increased, then distance between the fringes ____________.
A plane wavefront of wavelength `lambda`. is incident on a slit of width a. The angular width of principal maximum is ______.
In young 's double slit experiment the two coherent sources have different amplitudes. If the ratio of maximum intensity to minimum intensity is 16 : 1, then the ratio of amplitudes of the two source will be _______.
A physical quantity P is described by the relation p = a1/2 b2 c3 d-4. If the relative errors in the measurement of a, b, c and d respectively, are 2%, 1%, 3% and 5%, then the relative error in P will be ______.
In a Young's double-slit experiment, let β be the fringe width, and let I0 be the intensity at the central bright fringe. At a distance x from the central bright fringe, the intensity will be ______.
The fringe width in a Young's double slit experiment can be increased if we decrease ______.
In Fraunhofer diffraction pattern, slit width is 0.2 mm and screen is at 2 m away from the lens. If wavelength of light used is 5000 Å, then the distance between the first minimum on either side of the central maximum is ______. (θ is small and measured in radian)
Let a steel bar of length l, breadth b and depth d be loaded at the centre by a load W. Then the sag of bending of beam is ______.
(Y = Young's modulus of material of steel)
In Fraunhoffer diffraction experiment, L is the distance between the screen and the obstacle, b is the size of the obstacle and λ is the wavelength of the incident light. The general condition for the applicability of Fraunhoffer diffraction is ______.
Two coherent monochromatic light beams of amplitudes E10 and E20 produce an interference pattern. The ratio of the intensities of the maxim a and minima in the interference pattern is ______.
State the characteristics of a single slit diffraction pattern.
