Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Solution
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is the other name given to the principle of the mixtures?
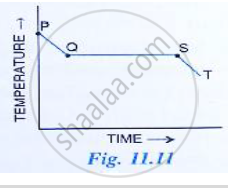
Fig 11. 11 shows the variation in temperature with time when some wax cools from the liquid phase to the solid phase.
(i) In which part of the curve, the wax is in liquid phase?
(ii) What does the part QS of the curve represent?
(iii) In which part of the curve, the wax will be the in the liquid as well as solid phase?
(iv) In which part of the curve, the wax is in solid phase?
The specific heat capacity of a substance A is 3,800 Jkg `"^(–1)K^(–1)` and that of a substance B is 400 `"^(–1)K^(–1)`. Which of the two substances is a good conductor of heat ? Give a reason for your answer.
Express -400C on the Fahrenheit scale.
Calculate the time taken by an immersion heater, which supplies energy at the rate of 7000 J/minute to raise temp. of 5 kg water from 22°C to 47°C.
Which contains more heat: 1 G water at 100°C or 1 g steam at 100°C? Give reason.
Why does the heat supplied to a substance during its change of state not cause any rise in its temperature?
What happens to the average kinetic energy of the molecules as ice melts at 0°C?
