Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What will happen if the price prevailing in the market is
(i) above the equilibrium price?
(ii) below the equilibrium price?
Solution
(i) If the market price is above the equilibrium price, there occurs the situation of excess supply.
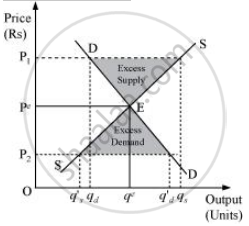
In the given figure, the equilibrium price and quantity is demoted by Pe and qe.
Let us assume that the market price (P1) is above the equilibrium price Pe. Now, according to the demand curve, the quantity demanded is qd. Whereas, according to the supply curve, the quantity supplied is qs. Thus, there exists a situation of excess supply equivalent to (qs − qd).
(ii) If the market price is below the equilibrium price, there occurs the situation of excess demand.
Let us assume that the market price P2 is below the equilibrium price Pe. According to the demand curve, quantity demanded is q′d. Whereas, according to the supply curve, the quantity supplied is q′s. So, it can be seen that there emerges the situation of excess supply equivalent to (q′d − q′s).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A market for a good is in equilibrium. There is simultaneous "increase" both in demand and supply of the good. Explain its effect on the market price
Market for a good is in equilibrium. There is simultaneous "decrease" both in demand and supply of the good. Explain its effect on market price
A market for a good is in equilibrium. The demand for the good 'increases'. Explain the chain of effects of this change.
A market for a good is in equilibrium. The supply of good "decreases". Explain the chain of effects of this change
A market for a product is in equilibrium. Demand for the product "decreases." Explain the chain of effects of this change till the market again reaches equilibrium. Use diagram
What is meant by 'excess supply' of a good in a market?
Explain its chain of effects on the market of that good. Use diagram
Draw average revenue and marginal revenue curves in a single diagram of a firm which can sell more units of a good only by lowering the price of that good. Explain.
Market for a good is in equilibrium. There is an ‘increase’ in demand for this good. Explain the chain of effects of this change. Use diagram.
Explain market equilibrium.
How are equilibrium price and quantity affected when income of the consumers increase.
How will a change in price of coffee affect the equilibrium price of tea? Explain the effect on equilibrium quantity also through a diagram.
How do the equilibrium price and the quantity of a commodity change when price of input used in its production changes?
Considering the same demand curve as in exercise 22, now let us allow for free entry and exit of the firms producing commodity X. Also assume the market consists of identical firms producing commodity X. Let the supply curve of a single firm be explained as
qSf = 8 + 3p for p ≥ 20
= 0 for 0 ≤ p < 20
(a) What is the significance of p = 20?
(b) At what price will the market for X be in equilibrium? State the reason for your answer.
(c) Calculate the equilibrium quantity and number of firms.
Answer the following question.
Show with the help of diagrams, the effect on equilibrium price and quantity when:
There is a fall in the price of substitute goods.
Answer the following question.
Show with the help of diagrams, the effect on equilibrium price and quantity when:
There is a rise in the prices of inputs.
Rate of interest on savings account is more than that on recurring account.
